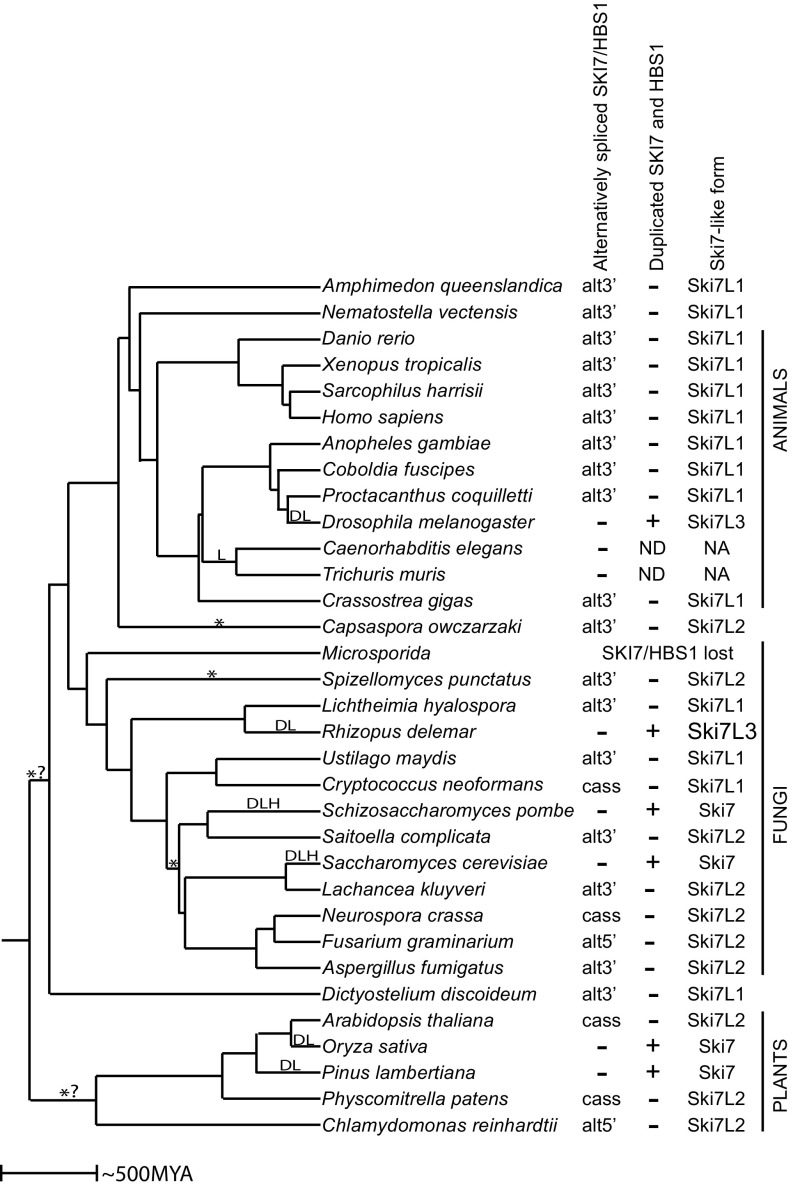
Fig. 2.
Alternative splicing of a single SKI7/HBS1 is conserved in diverse eukaryotes. The tree reflects the species tree, with branch lengths reflecting time of divergence as estimated by www.timetree.org/. D indicates a gene duplication event; L, a loss of alternative splicing; *, a switch between a Ski7 that contains or lacks the GTPase domain; H, a loss of the catalytic histidine; and *? indicates that it is not clear whether one change of alternative splicing occurred in the common ancestor of plants or in the common ancestor of animals and fungi. Alternative splicing patterns include the use of alternative 3′ splice sites (alt3′), the use of alternative 5′ splice sites (alt5′), and the use of a cassette exon (cass). N.A., not applicable; N.D, not detected. Ski7-like protein forms Ski7L1, Ski7L2, and Ski7L3 are defined in Fig. 3E.