Figure 2.
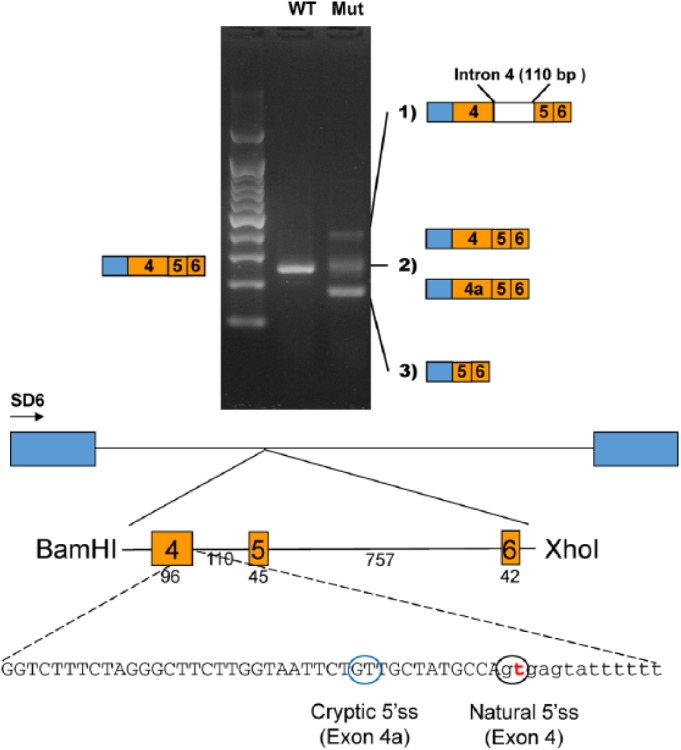
In vitro splicing assay. A genomic fragment, including exons 4, 5, and 6, was cloned into the pSPL3 splicing vector with the BamHI and XhoI restriction endonucleases. Boxes in the diagram indicate the exons in the pSPL3 vector. The number of base pairs (bp) are shown below the exons and the intron. Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction revealed 3 weaker amplicons in the mutant vector, as compared with 1 in the wild-type vector. Sequencing identified abnormal splicing products in the mutant instead of the normal splicing product in the wild type. The mutation in the natural 5′ splicing site (5′ss) activated a cryptic 5′ss, and a new exon sequence (exon 4a) was included in some mutant transcripts instead of the normal exon 4. mut, mutant; WT, wild type.
