Figure 3.
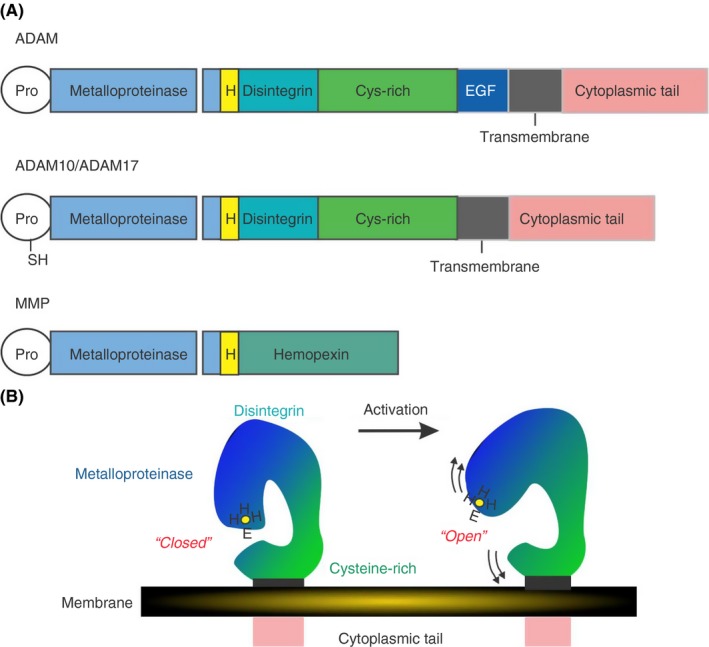
Domain structure of ADAMs. (A) ADAMs have a uniform domain structure with a prodomain that is removed prior to transport to the cell membrane, followed by a metalloproteinase, disintegrin,cysteine‐rich and epidermal growth factor‐like domains domains, a transmembrane domains and a cytoplasmic tail. ADAM10 and ADAM17 do not have EGF‐like domains and do have a free sulfhydryl (SH) group within the prodomain which may coordinate with the HEHH Zn2+ binding sequence within the metalloproteinase domain. (B) Analysis of the crystal structure of human ADAM10 [76] suggests a closed conformation of the enzyme under resting conditions where the cysteine‐rich domain occludes the metalloproteinase active site. Under conditions of activation, the metalloproteinase domain is freed and a substrate can gain access to the catalytic site
