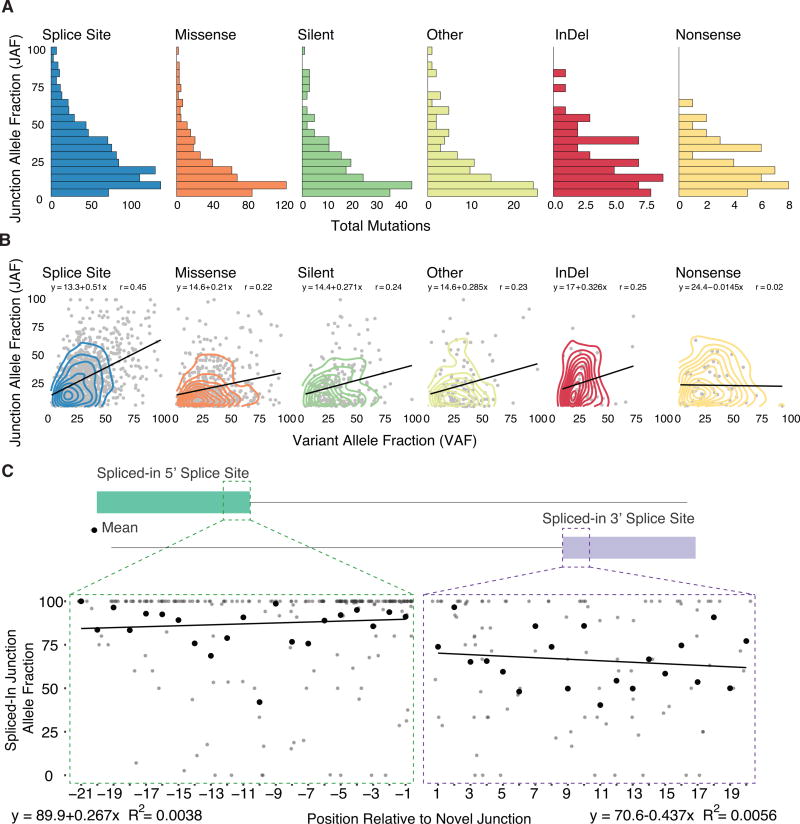
Figure 3. Junction Allele Fraction of Splice-Site-Creating Mutations.
(A) The junction allele fraction (JAF) is defined as the number of reads supporting the alternative spliced junction relative to total junction spanning reads. Distribution of JAF values separated by conventional annotation type.
(B) JAF versus DNA variant allele fraction (VAF) comparison by conventional annotation type. Most mutation types show a generally positive correlation between JAF and VAF values.
(C) Splice-site-creating mutations expressed in the newly created exon of the alternative splice junction. Comparison of mutation position relative to the percent of reads supporting the alternative junction and mutation (spliced-in JAF). The mean of each position is highlighted by the black point. For all positions, there is a strong correlation between the presence of the splice-site-creating mutation and the alternative splice junction.