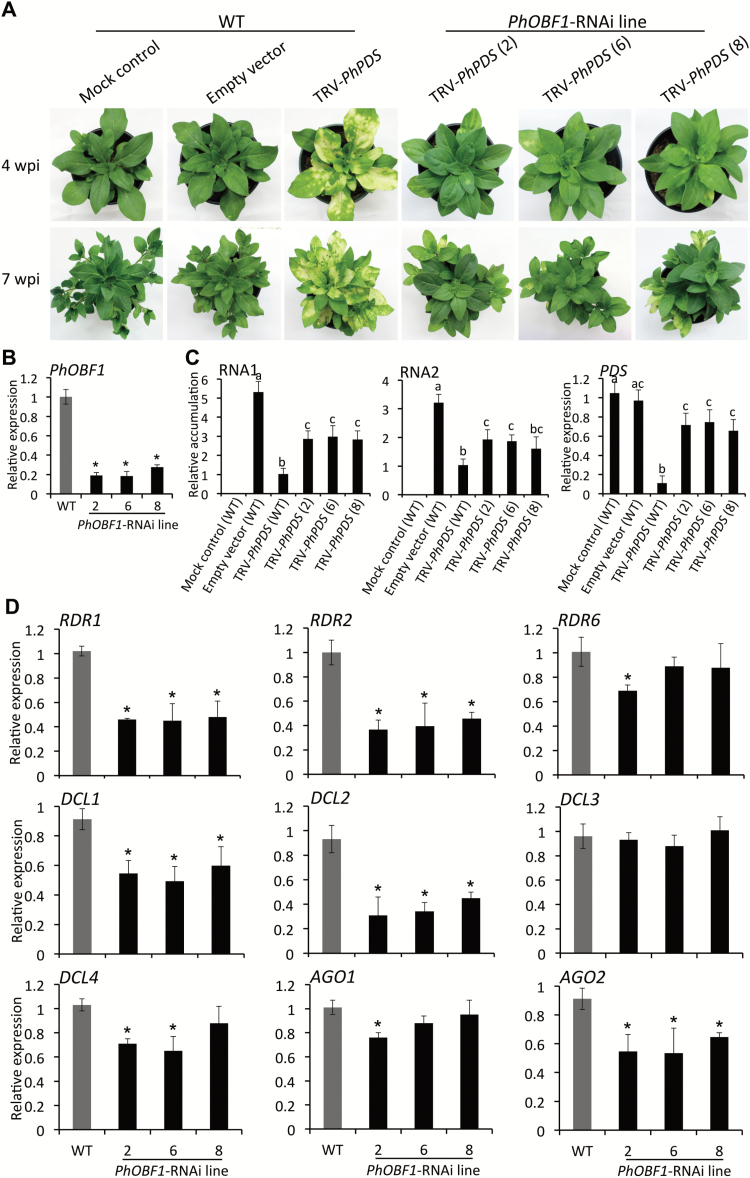
Fig. 4.
Impairment of leaf photobleaching phenotype of PDS silencing in PhERF2-RNAi lines inoculated with Agrobacterium bearing TRV-PhPDS. (A) Representative phenotypes of WT and PhOBF1-RNAi lines (2, 6 and 8) inoculated with non-transformed Agrobacterium (mock control), or Agrobacterium bearing a TRV empty vector and TRV-PhPDS construct. Photographs were taken at 4 and 7 weeks post-inoculation (wpi). (B) Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of transcript abundances of PhOBF1 in uppermost leaves of 4-week-old WT and PhOBF1-RNAi lines (2, 6 and 8). Expression levels were normalized to 26S rRNA. (C) Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of TRV (RNA1 and RNA2) accumulation and PDS transcript levels in uppermost leaves of WT and PhOBF1-RNAi lines (2, 6 and 8) at 4 wpi. Accumulation and transcript levels were standardized to 26S rRNA. (D) Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of transcript abundances of RNA silencing-related genes, including RDR1, RDR2, RDR6, DCL1, DCL2, DCL3, DCL4, AGO1, and AGO2, in uppermost leaves of 4-week-old WT and PhOBF1-RNAi lines (2, 6 and 8). 26S rRNA was used as internal standard. Error bars represent standard error of the mean from three biological replicates. Significance of difference was calculated using Duncan’s multiple range test (P<0.05) and shown as asterisks or different letters.