Figure 2.
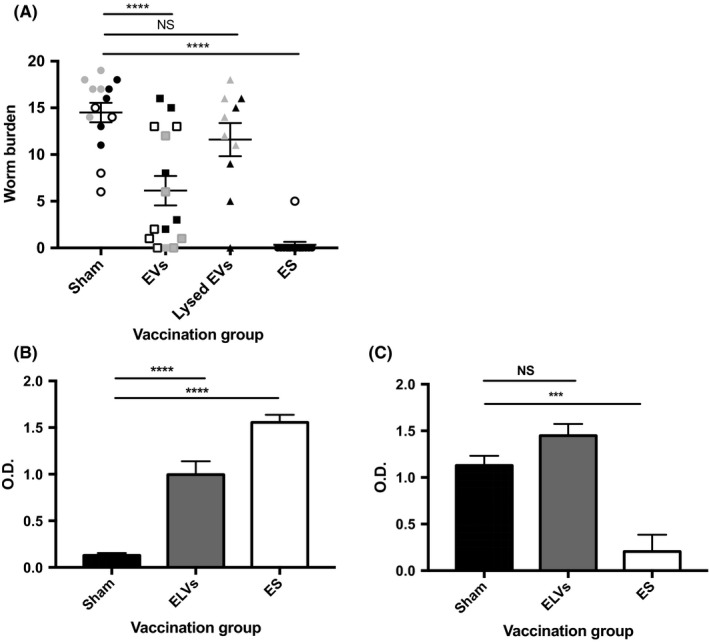
Vaccination with T. muris EVs induces a reduction in worm burden and a mixed Th1/Th2 response. Male C57BL/6 mice, n = 10 to 15 per group, were subcutaneously vaccinated with whole or lysed EVs, followed by a second vaccination 14 days later. The sham vaccination group received two saline injections, while the positive control group received two vaccinations with ES depleted of EVs. Mice were infected with 25 T. muris eggs by oral gavage. A, shows the worm burden at 32 days post‐infection. The data are pooled from three independent experiments (black, white and grey symbols indicate separate experiments). The IgG1 and IgG2a/c serum antibody responses to ES depleted of EVs were measured by ELISA and are displayed in B and C, respectively. The mean O.D. value (reading at 405 and 490 nm) for each vaccination group (sham, EV or ES vaccinated mice) is shown at 1:320 (IgG1) and 1:40 (IgG2a/c) serum dilution. Error bars show SEM, ****P < .0001, ***P < .001, NS = nonsignificant
