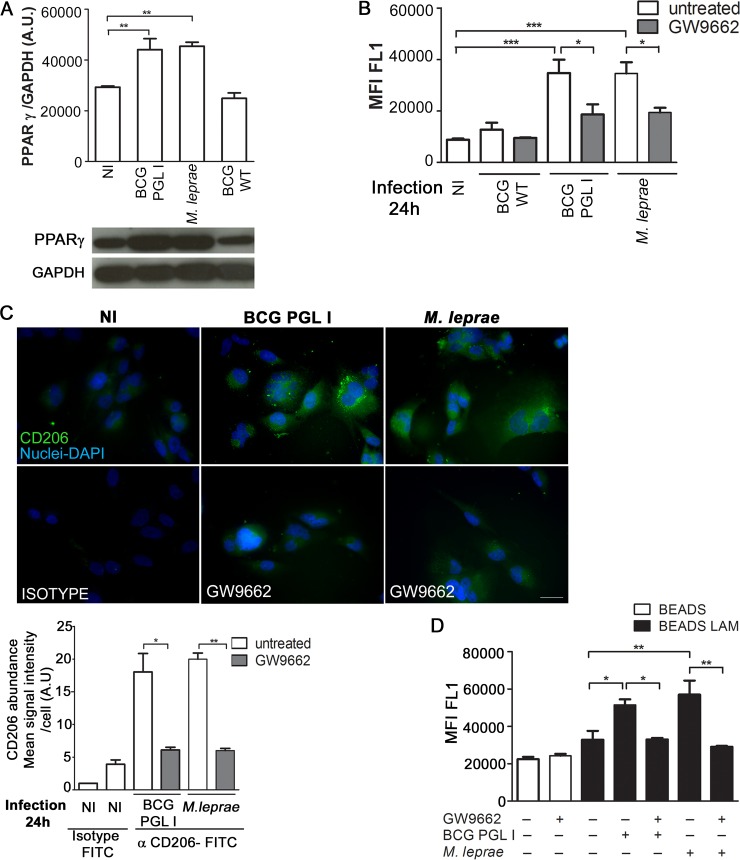
Fig 6. PGL I-producing mycobacterium induces CD206 expression in Schwann cells via PPARγ.
A. Total lysates (20μg per well) from SC cultures were subjected to Western Blotting using specific antibodies against PPARγ and GAPDH. A representative Western blot from three independent experiments is shown. The content of the bands was estimated by densitometric analysis; and relative expression was plotted in arbitrary units (A.U. = arbitrary units). B and C. SC were treated with the PPARγ antagonist GW9662 (5μM) for 30 minutes previous to a 24 h infection with either BCG WT, BCG PGL I, or M. leprae at MOI 50:1. CD206 expression was determined using flow cytometry and fluorescence microscopy by immunolabeling of CD206 with FITC conjugated anti-CD206 antibody (clone15-2, Mouse IgG1, κ1, Biolegend). Treatment with GW9662 decreased CD206 expression in SC. For microscopy, cells on coverslips were fixed with paraformaldehyde and stained with DAPI (blue) for nuclear localization. Images are representative of 3 independent experiments. Scale (white line) represents 10 μm. CD206 mean signal intensity per cell was quantified. D. SC were treated with GW9662 5μM for 30 minutes previous to 48 h stimulation with either uncovered beads or ManLAM-covered beads at a proportion of (50:1). Pre-stimulus with unlabeled M. leprae or BCG PGL I was carried out after treatment with the antagonist and one hour before the second stimulus. Internalization of the green fluorescent beads was determined by flow cytometry (FL1-A channel). Results are represented as mean ± SEM of three independent biological replicates. Statistical significance was calculated by ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test. *p < 0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001.