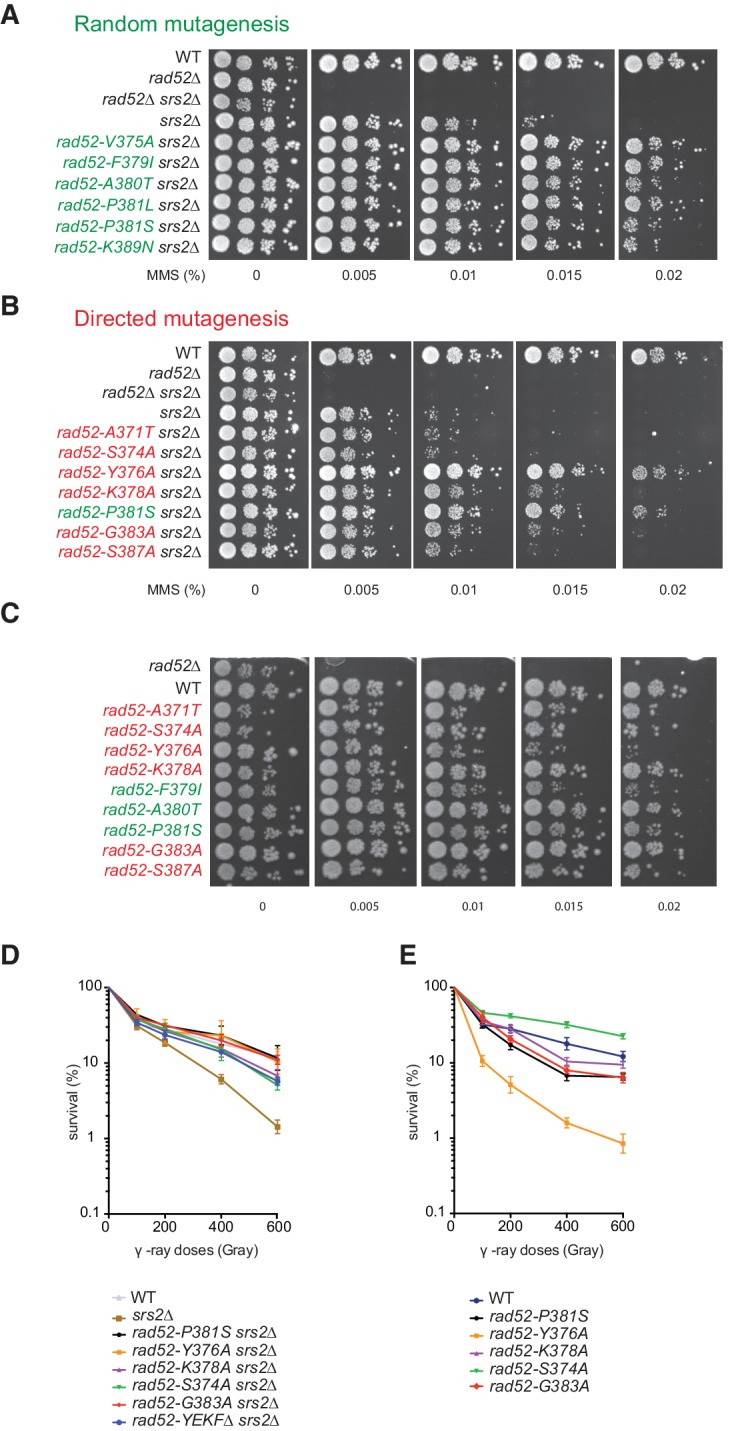
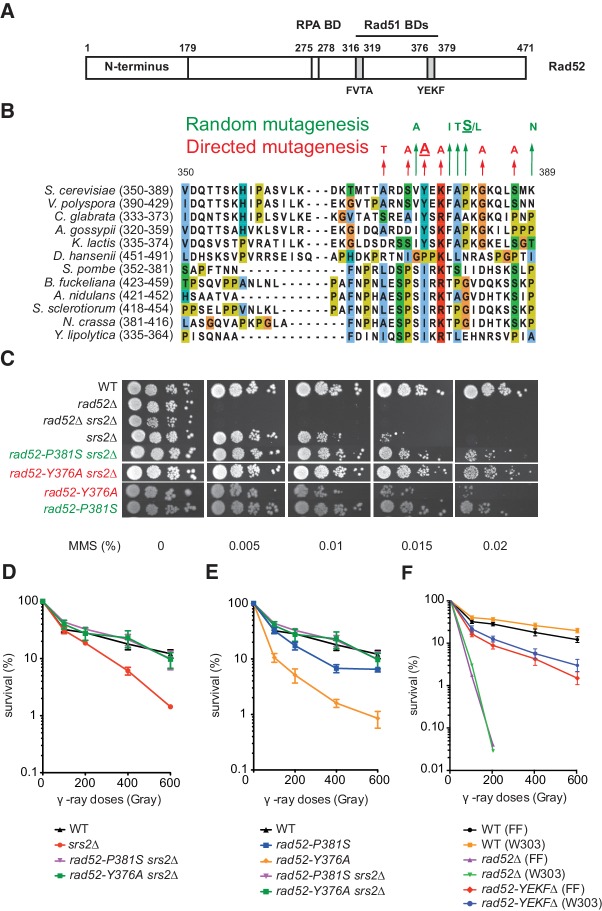
Figure 1. Mutations in the Rad51-binding domain of Rad52 suppress MMS and γ-ray sensitivity of Srs2-deficient cells.
(A) Primary structure of Rad52. The conserved N-terminus as well as the RPA and the Rad51 binding domains (BD) are shown. (B) The mutations selected from random and directed mutagenesis are indicated on the alignment of the region 350-389aa of S. cerevisiae Rad52 with that of Rad52 orthologs in 12 fungal species. The amino acid colors refer to the chemical character of the residues. The rad52-P381S and rad52-Y376A mutations are underlined. (C) Serial 10-fold dilutions of haploid strains with the indicated genotypes were spotted onto rich media (YPD) containing different MMS concentrations. The data presented are a selection from those in Figure 1—figure supplement 1. (D,E,F) Survival curves of haploid cells exposed to γ-ray. rad52-YEKF∆ cells were from two different genetic backgrounds: FF18733 (FF) and W303. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments.
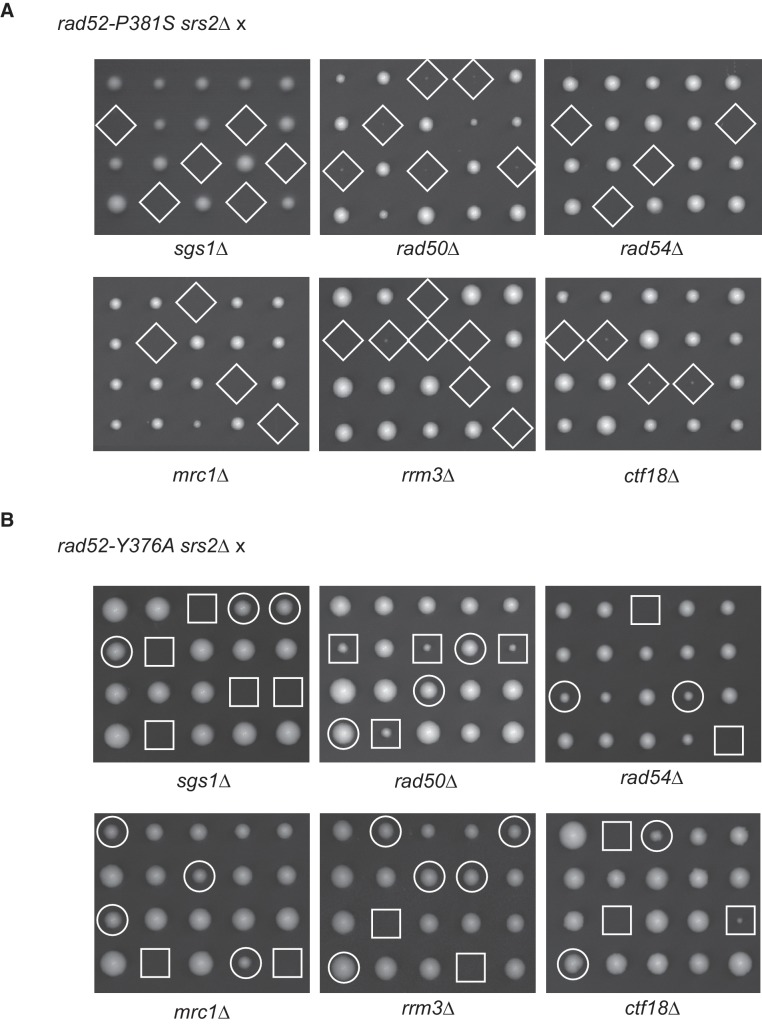
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. Mutations in the Rad51-binding domain of Rad52 suppress MMS and γ-ray sensitivity of Srs2-deficient cells.