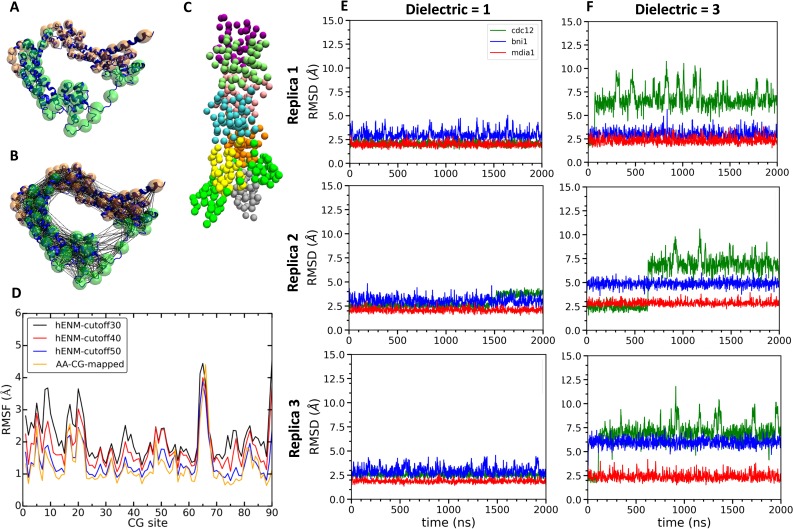
Figure 8. Construction and simulations of coarse-grained (CG) models of FH2 domains.
(A) Assignment of coarse-grained (CG) sites of the Cdc12 FH2 domain dimer by the EDCG method (FHL is green and FHT is orange). (B) Connection of CG sites by harmonic bonds defined by heteroENM and matched to the fluctuations observed in all-atom simulations. (C) CG model of the Cdc12 FH2 domains on a seven-mer actin filament. FH2 domains are shown in green, actin monomers are colored as follow: A1 (gray), A2 (yellow), A3 (orange), A4 (cyan), A5 (pink), A6 (lime) and A7 (purple). (D) Plot comparing root mean square fluctuations (RMSFs) of the CG sites of the Cdc12 FH2 dimer obtained from AA simulations (AA-CG mapped) with RMSFs of these sites in CG simulations using a range of cutoff distances for the harmonic springs that connect every CG site. The cutoff distance of 50 Å (blue) gives the best match with the RMSFs of AA simulations (yellow). (E, F) Time courses of the root mean squared displacements of the FH2 dimers from three independent CG simulations spanning two microseconds at low and high dielectric constant. (E) Dielectric constant is 1. (F) Dielectric constant is 3.