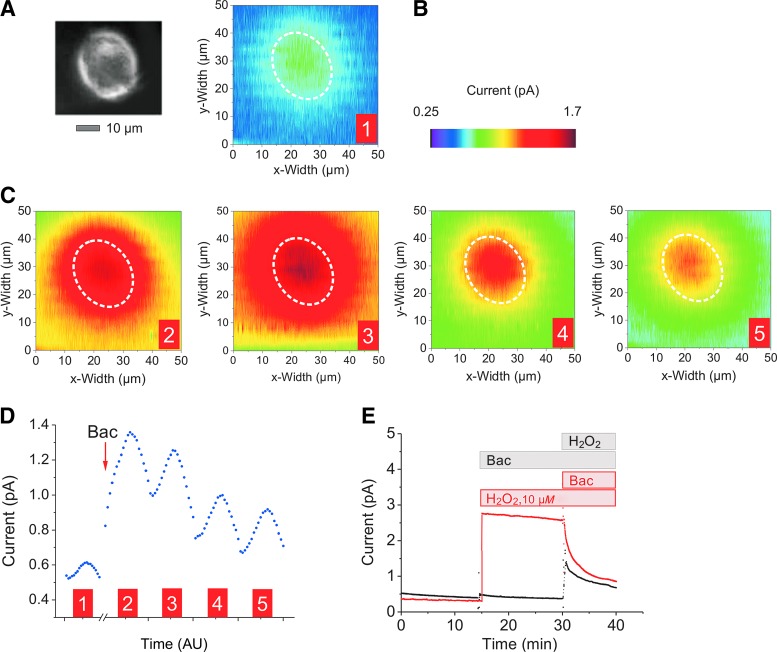
FIG. 5.
Respiratory burst of an MC after stimulation with Escherichia coli. 2D scans (B, C) of the cell in (A) and control experiments (E) were performed chronoamperometrically at 650 mV in PBS-I buffer using a 10 μm Pt-UME versus Ag/AgCl. (B, C). With the UME placed 5–8 μm above, the MC shown in (A) was measured in five consecutive 2D scans before (B) and after addition (C) of a cell-free E. coli supernatant in LB medium (Bac). Dashed white circles mark the position of the MC (A) during the scanning procedure. Scan settings: constant height; scanning rate x = 2 μm/s, 50-nm resolution; y = 2.5 μm, alternate mode; raw data, no compression. To complete one 2D scan, 8.5 min were needed. (D) Dotted blue traces quantify current values of the five 2D scan images in (B) and (C); numbers of waves 1–5 refer to the corresponding 2D scan numbers. Each 2D scan comprises 20 scan lines alternating in the x-direction, separated by 2.5 μm in the y-direction (meander scan). The mean current value of each scan line of the five 2D scans (5*20 scan lines = 100 mean values) is represented by one blue dot (D). (E) Control experiments (representative of n = 8 per condition). Addition of bacterial supernatant [Bac; same amount as in (C)] to blank PBS-I (black trace) and to PBS-I containing H2O2 (10 μM; red trace).