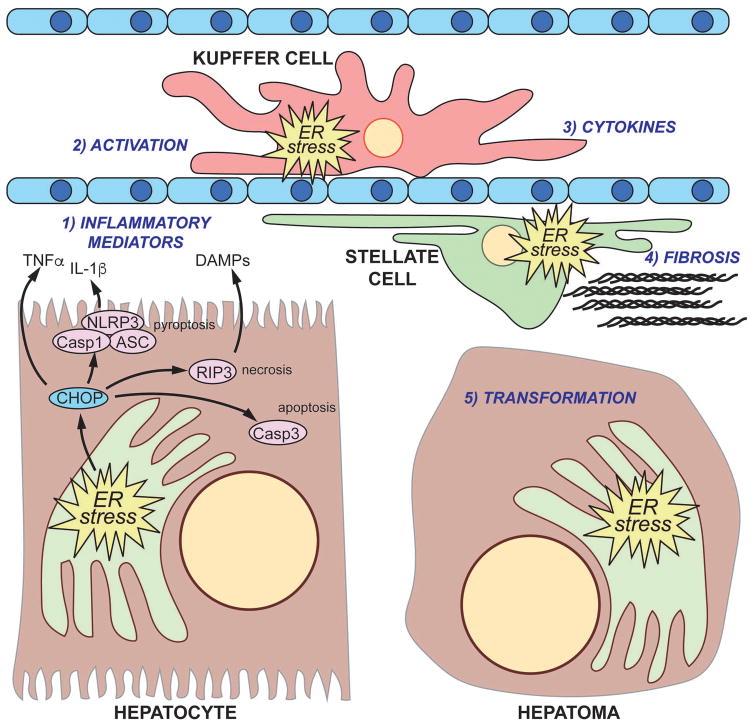
Figure 3.
The complex interplay between ER stress and liver damage and transformation
(1) Unremediable ER stress in hepatocytes can elicit cell death, which might proceed through apoptotic, necrotic, or pyroptotic pathways or a combination thereof. Hepatocytes subjected to ER stress also can secrete pro-inflammatory signals such as TNFα or other factors. Hepatocyte cell death stimulates macrophage activation (2) and secretion of inflammatory cytokines (3), and activation might represent its own ER stress in the macrophage. Likewise, inflammation promotes hepatic stellate cell activation (4), including production and extrusion of collagen through the secretory pathway. The combination of inflammatory cytokines and fibrotic deposition stimulates compensatory hepatocyte proliferation which, if unchecked, can promote tumorigenesis (5).