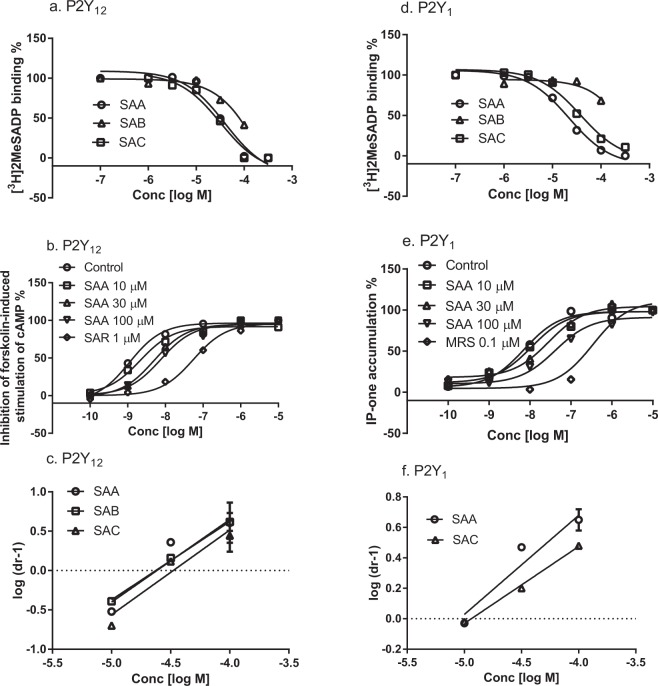
Figure 1.
Radioligand binding assays and functional assays showed that SAA and SAC can bind and antagonize both P2Y1 and P2Y12 receptors, while SAB can bind and antagonize only the P2Y12 receptor. (a) Displacement curves of SAA, SAB and SAC against [3H]2MeSADP binding to the P2Y12 receptor. (b) Functional antagonism by SAA of 2MeSADP-induced inhibition of foskolin-stimulated cAMP accumulation in U2OS cells expressing the P2Y12 receptor. (c) Schild plots of the antagonism of SAA, SAB and SAC at the P2Y12 receptors. (d) Displacement curves of SAA, SAB and SAC against [3H]2MeSADP binding to the P2Y1 receptor. (e) 2MeSADPinduced IP-1 accumulation in U2OS cells expressing the P2Y1 receptor (compared to MRS2500). (f) Schild plots of antagonism by SAA and SAC at the P2Y1 receptor. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM. The Ki values from binding experiments and KB values from Schild analyses of functional antagonism by SAA, SAB and SAC are listed in the text and are from at least three independent experiments. MRS, MRS2500; SAR, SAR216471.