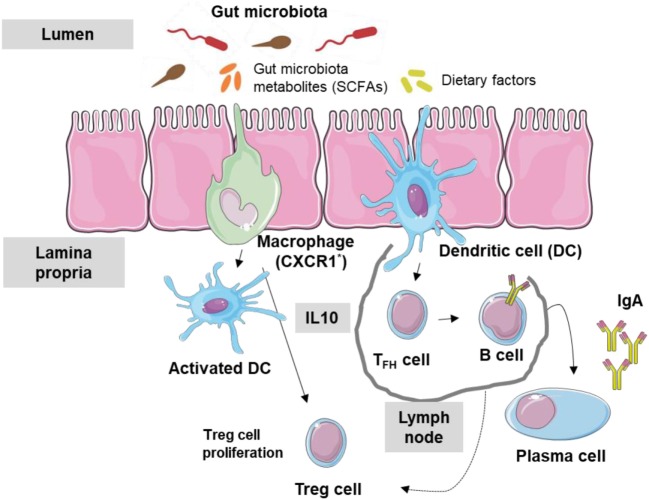
Figure 1.
Interaction between gut microbiota and immune system. Gut microbiota metabolites and dietary factors constitute the main antigen load of the gastrointestinal tract. Macrophages (CXCR1+) and dendritic cells (DCs) are stimulated and T regulatory (Treg) cells are activated by metabolic products such as short chain fatty acid (SCFA). Follicular T cells activate B cells inducing the production of IgA antibodies.