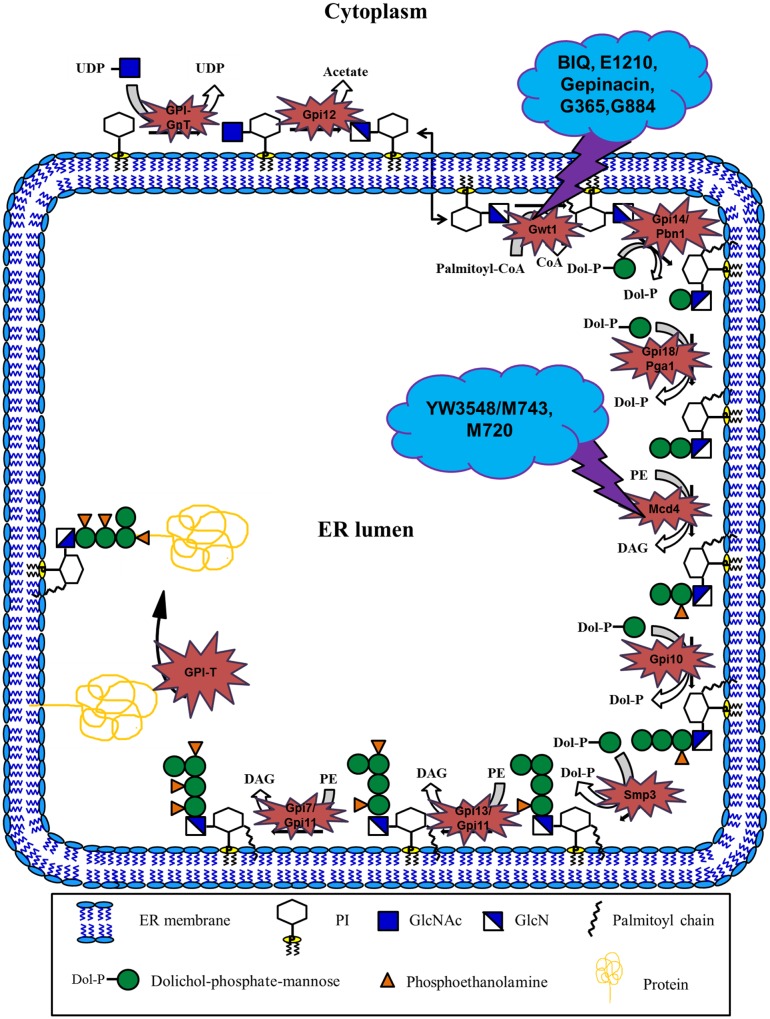
Figure 1.
Overview of GPI biosynthesis in yeast.
Notes: GPI biosynthesis is initiated on the cytoplasmic side of the ER by the transfer of N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) from UDP-GlcNAc to membrane bound phosphatidylinositol (PI), forming N-acetylglucosaminylphosphatidylinositol (GlcNAc-PI). This reaction is catalyzed by GPI-GlcNAc transferase complex (GPI-GnT) comprising of six core subunits – Gpi3, Gpi2, Gpi15, Gpi19, Gpi1 and Eri1, of which Gpi3 acts as the catalytic subunit. GlcNAc-PI is then de-N-acetylated to glucosaminylphosphatidylinositol (GlcN-PI) by GlcNAc-PI de-N-acetylase (Gpi12), followed by flipping of GlcN-PI to the lumenal side of the ER by yet to be identified flippase. All subsequent reactions of GPI biosynthesis take place on the lumenal side of the ER. GlcN-PI is acylated, usually by palmitoyl group, on the 2-position of inositol by acyl-CoA dependent inositol acyltransferase (Gwt1) generating GlcN-(acyl)PI. First and second mannoses are then added sequentially to the GlcN-(acyl)PI by the GPI-α1,4mannosyltransferase-I (Gpi14/Pbn1) and GPI-α1,6mannosyltransferase-II (Gpi18/Pga1) respectively, leading to the formation of Man-Man-GlcN-(acyl)PI intermediate. This is followed by the transfer of phosphoethanolamine group (EtNP) to the 2-position of first mannose by the GPI-phosphoethanolaminetransferase-I (Mcd4) generating Man-(EtNP)Man-GlcN-(acyl)PI. Third and fourth mannose additions are subsequently carried out by the GPI-α1,2mannosyltransferase-III (Gpi10) and GPI-α1,2mannosyltransferase-IV (Smp3) respectively, resulting in the formation of Man-Man-Man-(EtNP)Man-GlcN-(acyl)PI. Phosphoethanolamine moieties are then added sequentially to the 6-position of third and second mannose respectively by the GPI-phosphoethanolaminetransferase-III (Gpi13/Gpi11) and GPI-phosphoethanolaminetransferase-II (Gpi7/Gpi11), resulting in the formation of complete GPI precursor, Man-(EtNP)Man-(EtNP)Man-(EtNP)Man-GlcN-(acyl)PI. Dolichol-phosphate-mannose (Dol-P-Man) and phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) serve as the donors for the mannoses and the phosphoethanolamine groups respectively in the mannosylation and phosphoethanolamine transfer reactions. Finally, complete GPI precursor is transferred to the C-termini of the proteins bearing GPI signal sequences with the help of GPI transamidase (GPI-T). This multisubunit enzyme complex comprises of five subunits, namely, Gpi8, Gaa1, Gpi17, Gpi16 and Gab1, of which Gpi8 acts as the catalytic subunit. GPI transamidase covalently links the preformed GPI precursor to the protein through the amino group of the phosphoethanolamine moiety attached to the third mannose (Ref. 48). Gwt1 and Mcd4 inhibitors, which are the central focus of this review, are also shown in the schematic with details in the text.