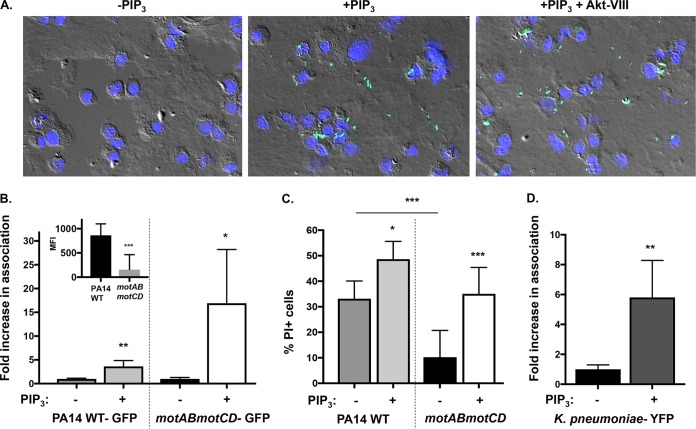
FIG 9.
PIP3 significantly increases binding of nonmotile bacteria to phagocytes. (A) Representative images of WT BMDCs pretreated with 12 μM PIP3 with or without 5 μM Akt inhibitor VIII and incubated with GFP-expressing PA14 motAB motCD (green) at an MOI of 10 (magnification, ×40). The nuclei of BMDCs are stained with 4′,6′-diamidino-2-phenylindole (blue), and cells are viewed by differential interference contrast overlay. (B) Relative association of GFP-expressing PA14 WT or motAB motCD bacteria with PIP3-pretreated murine WT BMDCs, quantitatively measured by FACS analyses. PIP3-dependent increases in bacterial association with BMDCs are shown as the fold increase compared to the level of association in the absence of PIP3 pretreatment. The relative association of GFP-expressing PA14 WT or motAB motCD bacteria to BMDCs in the absence of PIP3 pretreatment is also shown (B, inset). (C) WT BMDCs either untreated or pretreated with PIP3 were assayed for relative cellular cytotoxicity following infection with the PA14 WT or motAB motCD strain (MOI of 10) for 45 min. BMDC cellular cytotoxicity was analyzed by propidium iodide (PI) staining followed by flow cytometric analysis. (D) Flow cytometry to assay KPPR1-YFP bacterial association with murine WT BMDCs pretreated with PIP3. The data were normalized in the same manner as described for panel B. All data were analyzed using an unpaired t test with Welch's correction (B and D) or one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc analyses (C) and are representative of at least two independent biological experiments (n ≥ 8). ***, P ≤ 0.0005; **, P ≤ 0.005; *, P ≤ 0.05; ns, not significant, for results compared to those without PIP3 treatment.