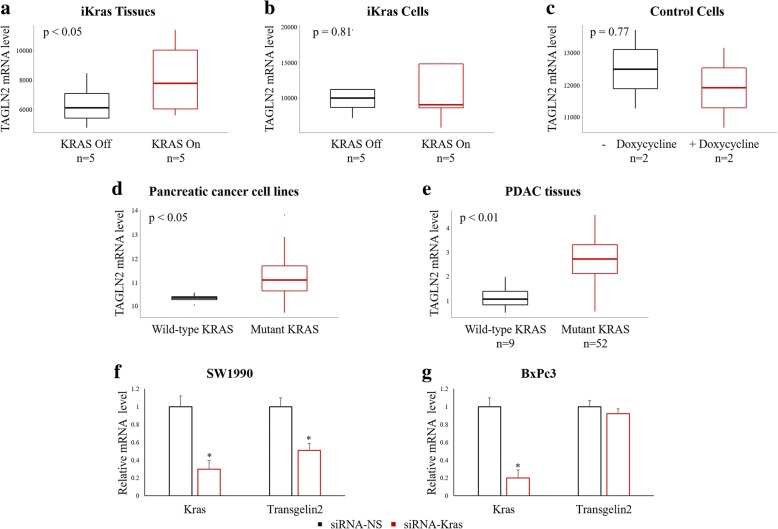
Fig. 1.
KRAS mutation induces transgelin-2 expression. a. The mRNA level of transgelin-2 was analyzed in tissues from tetO_LSL-KRASG12D/p48-Cre/ p53L/L mice. The mice were kept on doxycycline for 2 weeks until obvious tumor formation. Half of the animals were pulled off doxycycline for 24 h. KRAS on indicated induction of expression of KRAS by doxycycline, whereas KRAS off was without KRAS expression. b. The mRNA level of transgelin-2 was analyzed in primary cells derived from tetO_LSL-KRASG12D/p48-Cre/p53L/L mouse model. The primary cells were cultured in the presence or absence of doxycycline for 24 h and total cellular RNA was prepared. c. The mRNA level of transgelin-2 was analyzed in primary cells derived from tetO_LSL-KRASG12D without crossing with p48cre and p53L/L. The primary cells were cultured in the presence or absence of doxycycline for 24 h and total cellular RNA was prepared. d. The mRNA level of transgelin-2 was analyzed in CCLE datasets. Cell lines were categorized by KRAS G12 codon status. The “wild-type KRAS” group indicates that the KRAS gene is either wild-type or wild-type at the G12 codon. The “mutant KRAS” group indicates mutations at the G12 codon. Totally, there are 5 cell lines in “wild-type KRAS” group and 30 cell lines in “mutant KRAS” group. e. RNA was purified from PDAC tissues. The mRNA level of transgelin-2 was analyzed by qPCR. f-g. SW1990 and BxPc3 cells were transfected with siRNA-KRAS or siRNA-NS for 24 h. The mRNA level of transgelin-2 or KRAS were analyzed by qPCR. *p < 0.05 compared with the siRNA-NS group