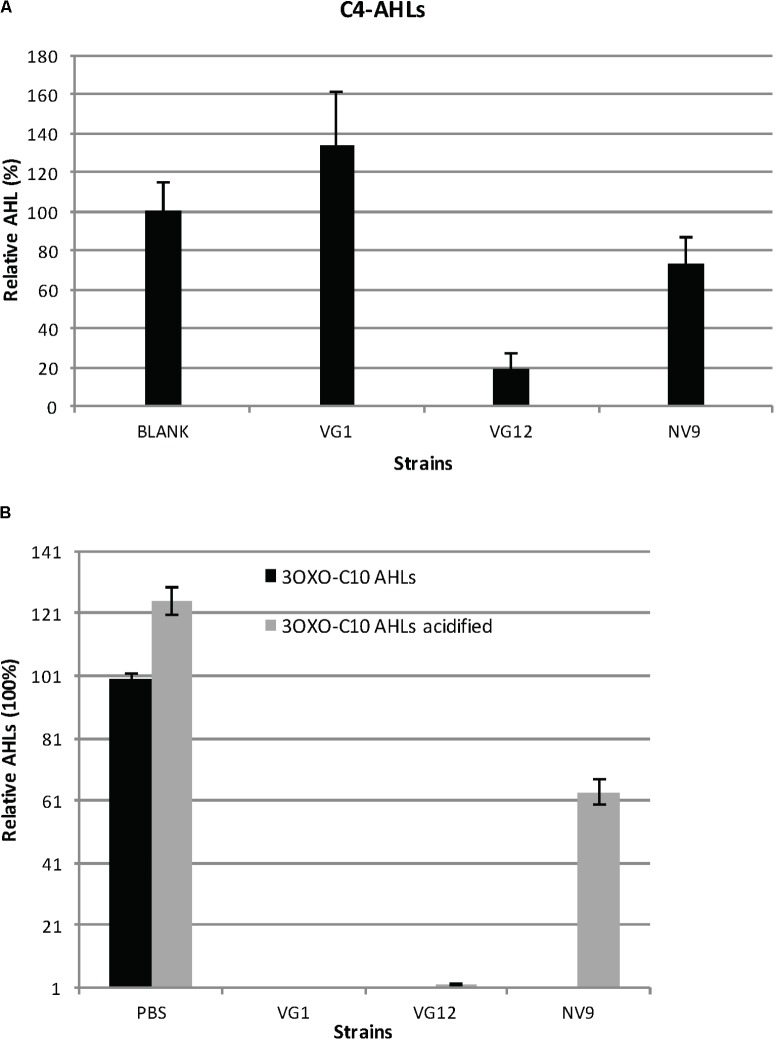
FIGURE 2.
Degradation and acidification of AHLs. (A) Relative amount of C4-AHLs degraded by the three isolates is given. For quantification, the C4-AHLs were extracted with ethyl acetate and subsequently dried and re-suspended in acetonitrile for injection in HPLC-MS. Cell-free PBS served as the negative control (100%). Experiments were performed in triplicate; error bars represent the standard deviation of the mean value. Student’s t-test showed significant reduction in the amount of C4-AHLs by VG12 (p-value = 0.003) and NV9 (p-value = 0.03). No significant degradation of C4-AHLs by VG1 was observed (p-value = 0.11). (B) Acidification of 3OXOC10-AHLs after incubation with QQ bacteria. Relative amount of AHLs before and after acidification is given. Black bars represent the amount of AHLs after incubation with PBS (negative control is 100%) or QQ bacteria. Gray bars represent the amount of AHLs recovered after acidification. Error bars represent the standard deviation for the three independent replicates.