Figure 6. BECC adjuvanted rF1-V vaccine protects mice from lethal Yp challenge.
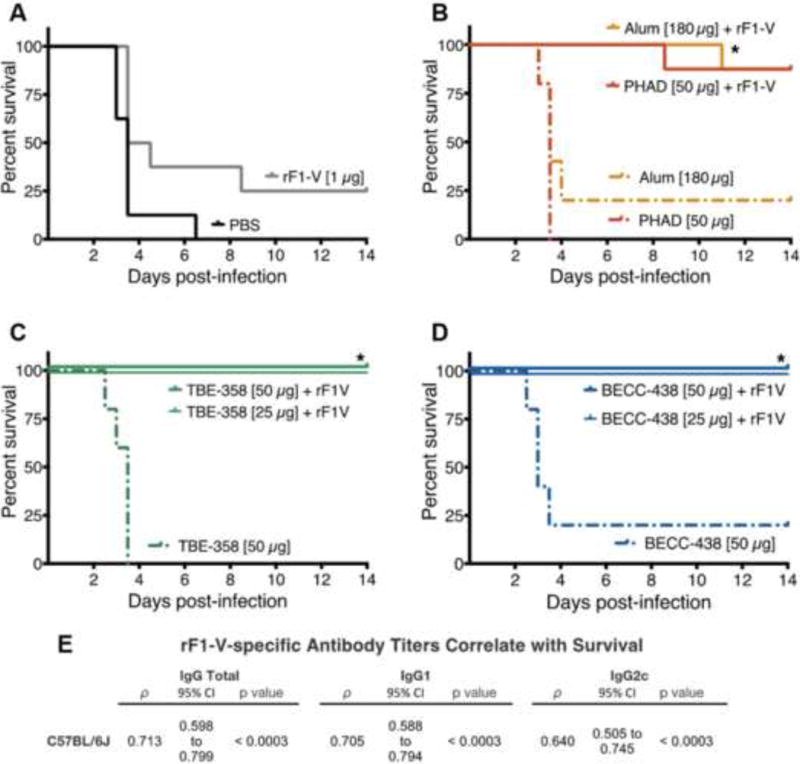
C57BL/6J mice were immunized intramuscularly on day 0 and day 14, and were challenged I.P. on day 36 with Yp CO92− (98 ± 16 or 101 ± 9 CFUs) and Fe(II) (1 μg). (A) PBS-immunized mice (n = 8, p = 0.267); (B) alhydrogel- (n = 8, p = 0.046) and PHAD-adjuvanted (n = 8, p = 0.055) treatment groups; (C) BECC438 50 μg (n= 8, p = 0.015) and 25 μg (n = 5, p = 0.089); and (D) TBE358 50 μg (n = 8, p = 0.015) and 25 μg TBE358 (n = 5, p = 0.089). Survival curves are pooled from two independent experiments. The log-rank (a.k.a. Mantel-Cox) pairwise test was used to compare the survival of the PBS and adjuvanted-rF1-V treatment groups to the antigen-alone control group. Bonferri-adjusted p-values were used to correct for multiple comparisons (K = 7) (N = 78, n = 5 or 8) (* = p < 0.05). (E) Survival was correlated with the rF1-V-specific IgG-subtype titer (n = 102, each) on day 28 by Spearman’s correlation analysis. The Spearman’s coefficient, ρ, 95% confidence interval, and Bonferroni-adjusted p-values (α = 0.05, K = 3) are presented. All rF1-V-specific IgG-subtype titers showed a significant, positive, and moderate correlation with survival.
