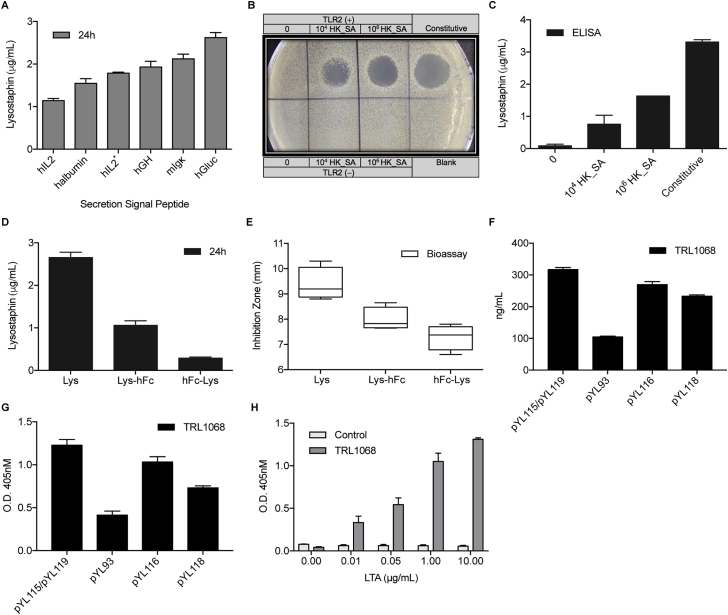
Figure S2.
Lysostaphin Secretion, Expression, and Further Modifications, Related to Figure 3
(A) Screening for optimal signal peptide that facilitates lysostaphin secretion. HEK293 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding constitutive lysostaphin expression directed by various signal peptides for secretion. hGLuc (pYL48, PhCMV-hGLuc-Lys-pA); hGH (pYL33, PhCMV-hGH-Lys-pA); hIL2 (pYL49, PhCMV-hIL2-Lys-pA); hIL2∗ (pYL51, PhCMV-hIL2∗-Lys-pA); halbumin (pYL50, PhCMV-halbumin-Lys-pA); mIgκ (pYL52, PhCMV-mIgκ-Lys-pA). Lysostaphin levels were quantified by ELISA after 24 hr.
(B) Spot-on-lawn assay for staphylolytic activity. Lytic zones developed on a lawn of S. carnosus at 24 hr after sample application. Samples (30 μL) were derived from HEK293 cells transfected with pYL25/pYL30/pYL75 (TLR2 (+)), pcDNA3.1(+)/pYL48 (Constitutive), pYL25/pcDNA3.1(+)/pYL75 (TLR2 (−)) and pYL25/pYL30/pYL3 (Blank), and induced with 104 and 106 cells/mL of HK_SA for 48 hr.
(C) Lysostaphin expression in HEK293 cells transfected with pYL25/pYL30/pYL75 (PAP-1 × 5-NF-κB × 5-IFNβmin-hGLuc-Lys-pA) or pcDNA3.1(+)/pYL48 (Constitutive), and induced with 104 and 106 cells/mL of HK_SA for 48 hr.
(D) Expression of lysostaphin fusion proteins with human IgG-Fc fragment (hFc). HEK293 cells were transfected with lysostaphin (Lys; pYL48, PhCMV-hGLuc-Lys-pA), Lysostaphin C-terminally fused with hFc (Lys-hFc; pYL72, PhCMV-hGLuc-Lys-hFc-pA) or Lysostaphin rN-terminally fused with hFc (hFc-Lys; pYL69, PhCMV-hGLuc-hFc-Lys-pA), and cultivated for 24 hr before sampling for lysostaphin expression.
(E) Antimicrobial activity of lysostaphin-fusion proteins. Bioassay toward MRSA was performed with cell supernatants from Lys (pYL48)-, Lys-hFc (pYL72)-, or hFc-Lys (pYL69)-transgenic HEK293 cells after 24 hr.
(F) The influence of linker sequence on the expression of human TRL1068. HEK293 cells were transfected with pYL115/pYL119 (PhCMV-hTRL1068-HC-pA/PhCMV-hTRL1068-LC-pA), pYL93 (PhCMV-hTRL1068-HC-RKRRP2A-LC-pA), pYL116 (PhCMV-hTRL1068-HC-RKRRF2A-LC-pA) or pYL118 (PhCMV-hTRL1068-HC-RAKRF2A-LC-pA), and sampled after 24 hr for the determination of hTRL1068 expression.
(G) Validation of hTRL1068 activity. Titration ELISA assay was used for the verification of the binding of TRL1068 to the epitope (AARKGRNPQTGKEID) contained in Staphylococcus aureus histone-like DNA-binding protein. Samples were derived from HEK293 cells transfected with pYL115/pYL119, pYL93, pYL116, or pYL118 after 24 hr.
(H) Dose-dependent regulation on hTLR1068 activity. Titration ELISA assay of TRL1068 binding to the epitope contained in Staphylococcus aureus histone-like DNA-binding protein.
Cell supernatants were taken from non-transfected HEK293 cells (Control) or cells transfected with pYL25/pYL30/pYL117 (P[NF-κB’-NF-κB]1-IFNβmin-hTRL1068-HC-RKRRF2A-LC-pA) (TRL1068) and induced with LTA at increasing concentrations for 72 hr. All data are means ± SD (n ≥ 3).