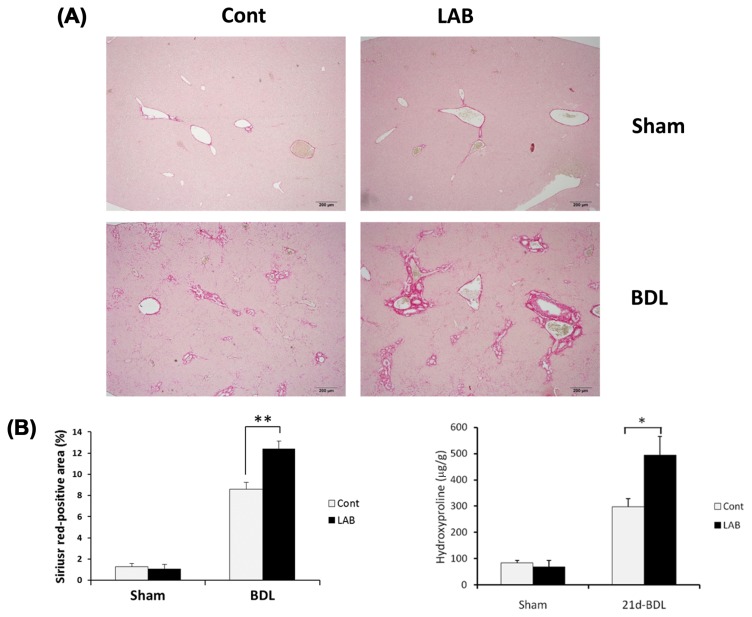
Fig. 1.
Administration of LAB exacerbates BDL-induced liver fibrosis. (A–B) Control or LAB-administered mice underwent sham operation (n = 4 per group) or BDL for 21 days (n = 8 per group). Fibrillar collagen deposition was determined by quantification of the Sirius red-positive area and hydroxyproline contents. LAB administration induced significant increase of Sirius red-positive area and hydroxyproline contents compared with control group. Data are presented as means ± SEM per group. Two-tailed Student’s t-test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. Original magnification, ×200 (Sirius-Red).