Figure 5.
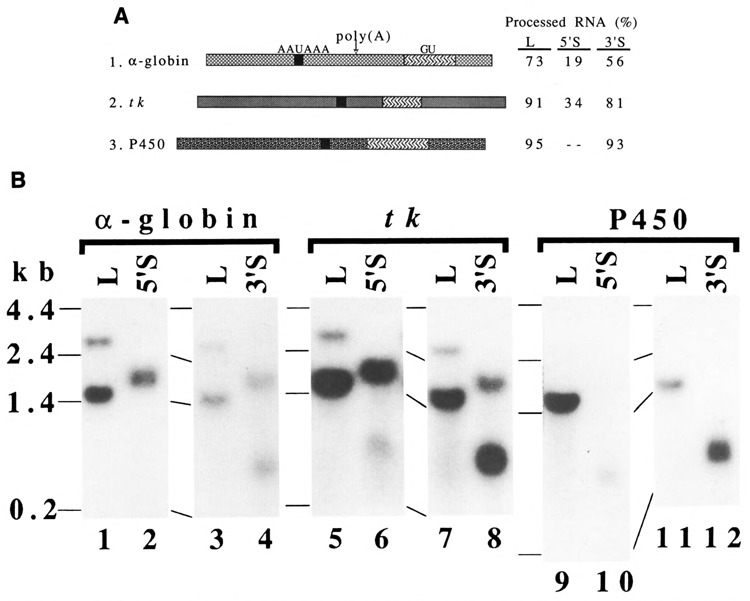
Other poly(A) signals for distance-dependent RNA 3′ end formation. A. Structures of poly(A) signals and the efficiency of RNA 3′ end formation at the poly(A) sites. The poly(A) signals for the mouse α-globin gene (Nishioka and Leder, 1979), the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase (tk) gene (Wagner et al., 1981), and the rat NADPH-cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase gene (Porter et al., 1990) are shown by  ,
,  , and
, and  , respectively. The downstream elements of the tk poly(A) signal were defined by others (Zhang et al., 1986). The GU-rich sequences downstream from the poly(A) sites in the α-globin and P450 oxidoreductase genes were determined by sequence analysis. Variation was the largest, 34% ± 13 (mean ± s.d.), for tk; and the smallest, 91% ± 5, for tk. Some data were mean values of two experiments. The percentage of processed RNA at the P450 poly(A) signal in the 5′S construct was not determined, because of low expression of RNA. When the level of total RNA from the L construct was taken as 1.0 in each set, relative levels of total RNA for other constructs were as follows: α-globin (L: 5′S: 3′S = 1: 1.2 :1.3), tk (L: 5′S: 3′S = 1: 0.6 :1.3), and P450 (L: 3′S = 1: 0.7). See the legend of Figure 2A for other symbols B. Northern blot analyses. D17 cells were transfected with the indicated constructs. See the legend of Figure 2B for other descriptions.
, respectively. The downstream elements of the tk poly(A) signal were defined by others (Zhang et al., 1986). The GU-rich sequences downstream from the poly(A) sites in the α-globin and P450 oxidoreductase genes were determined by sequence analysis. Variation was the largest, 34% ± 13 (mean ± s.d.), for tk; and the smallest, 91% ± 5, for tk. Some data were mean values of two experiments. The percentage of processed RNA at the P450 poly(A) signal in the 5′S construct was not determined, because of low expression of RNA. When the level of total RNA from the L construct was taken as 1.0 in each set, relative levels of total RNA for other constructs were as follows: α-globin (L: 5′S: 3′S = 1: 1.2 :1.3), tk (L: 5′S: 3′S = 1: 0.6 :1.3), and P450 (L: 3′S = 1: 0.7). See the legend of Figure 2A for other symbols B. Northern blot analyses. D17 cells were transfected with the indicated constructs. See the legend of Figure 2B for other descriptions.
