Figure 7.
Transgenic Bcl2 Causes Uncontrolled Expansion of Pten-Deficient B Cells
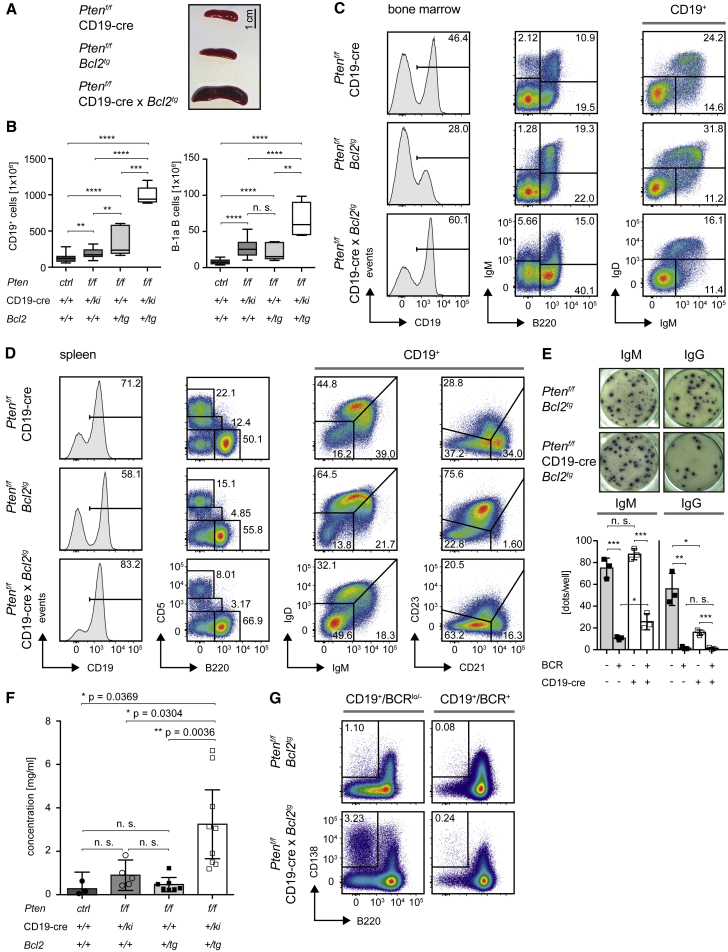
(A) Macroscopic appearance of spleens from Ptenf/f × CD19-cre, Ptenf/f × Bcl2tg, and Ptenf/f × CD19-cre × Bcl2tg mice sacrificed at the age of 10 weeks.
(B) Absolute numbers of CD19+ and B-1a B cells in Ptenf/f x CD19-cre x Bcl2tg (n = 5) and Ptenf/f x Bcl2tg (n = 5) compared to the Ptenf/f x CD19-cre and control mice already shown in Figures 1C and 5F (median ± quartile and range).
(C and D) Cells freshly isolated from spleens (C) and bone marrow (D) of Ptenf/f × CD19-cre, Ptenf/f × Bcl2tg, and Ptenf/f × CD19-cre × Bcl2tg mice were analyzed by flow cytometry for surface expression of the indicated markers. Representative data are shown from at least 5 mice sacrificed and analyzed at the age of 10 weeks.
(E) ELISpot assay for secretion of IgM and IgG, respectively. IgM−/lo/IgD− splenic B cells derived from mice of the indicated genotypes were FACS-purified and their capacity to secrete antibody was analyzed in triplicate after 16–24 hr of incubation (top). Numbers of dots in the triplicates were quantified (bottom), mean ± SD.
(F) IgM levels measured in sera from Ptenf/f × CD19-cre × Bcl2tg (n = 9), Ptenf/f × Bcl2tg (n = 7), Ptenf/f × CD19-cre (n = 5), and control mice (n = 3) (mean ± SD).
(G) Splenocytes from Ptenf/f × CD19-cre, Ptenf/f × Bcl2tg, and Ptenf/f × CD19-cre × Bcl2tg mice were analyzed by flow cytometry for surface expression of CD138 and B220 in the BCR+ (CD19+/B220+/IgM+/IgD+) and BCR−/lo (CD19+/B220+/IgM−/lo/IgD−) population of B cells.
See also Figure S7.