Figure 3.
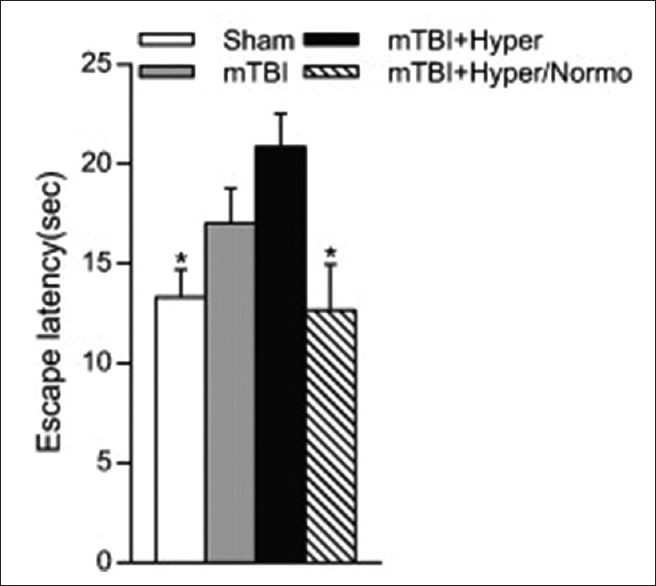
Effects of temperature manipulations on water maze performance. Analysis of escape latency on day 4 of testing 2 weeks postinjury. Hyperthermic mild traumatic brain injury animals had significantly longer escape latencies as compared to sham animals or hyperthermic/normothermic mild traumatic brain injury animals. *P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA and Tukey's post hoc analysis. Reprinted from Experimental Neurology, Vol 263, Emergence of cognitive deficits afer mild traumatic brain injury due to hyperthermia, pages 254-262, 2015, with permission from Elsevier
