Figure 4. TNFα-treatment of mo-DCs affects TEM and VLA-4 activity.
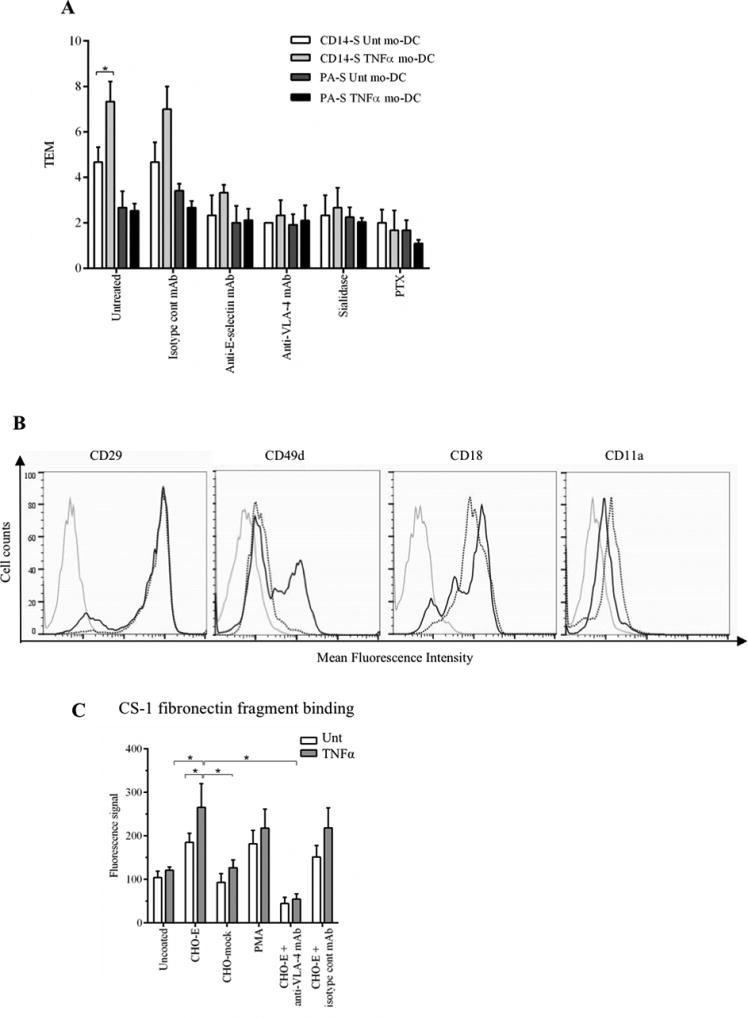
(A) Transendothelial migration (TEM) assay of untreated (Unt) and TNFα-treated CD14-S and PA-S mo-DCs. Both CD14-S and PA-S mo-DCs were left untreated or treated with TNFα for 2 days (after 5 days of differentiation). The relative TEM value was calculated as the ratio of transmigrated cells on TNFα-stimulated HUVECs compared with cells transmigrated on non-stimulated HUVECs. TEM values were analyzed for mo-DCs preincubated with isotype mAb, for HUVECs preincubated with function blocking anti-E-selectin mAb clone 68-5H1, for mo-DCs preincubated with function blocking anti-VLA-4 mAb HP2/1, and for mo-DCs treated with sialidase or PTX. (B) Flow cytometry analysis of cell surface expression of integrins VLA-4 and LFA-1 on CD14-S mo-DCs. Histograms show the staining in untreated (dotted black line) and TNFα-treated (solid black line) mo-DCs. Grey lines represent isotype control. (C) Analysis of CD14-S mo-DCs binding to CS-1 fibronectin fragment. Adhesion of untreated (Unt) or TNFα-treated CD14-S mo-DCs (TNFα) to CS-1 peptide was assessed following incubation of mo-DCs on plates containing monolayers of E-selectin-transfected CHO cells (CHO-E), mock transfected CHO (CHO-mock), or plates containing no CHO cells (uncoated). After incubation, cells were collected for binding to CS-1 peptide coated on plates. The number of CS-1-adherent cells was quantified by light absorbance (595 nm) following crystal violet staining. Cells activated with PMA (positive control) bound avidly to CS-1, and preincubation of cells on CHO-E markedly augmented binding to CS-1. Incubation with anti-VLA-4 blocking antibody (HP2/1) for the last 15 min of CHO-E engagement (CHO-E+anti-VLA-4 mAb) abrogated binding to CS-1. Values are mean ± SD (minimum of n=4). Statistically significant differences (P ≤ 0.05) related to CHO-E engagement are indicated by brackets and asterisks.
