Figure 3. Generation and characterization of human properdin transgenic mice.
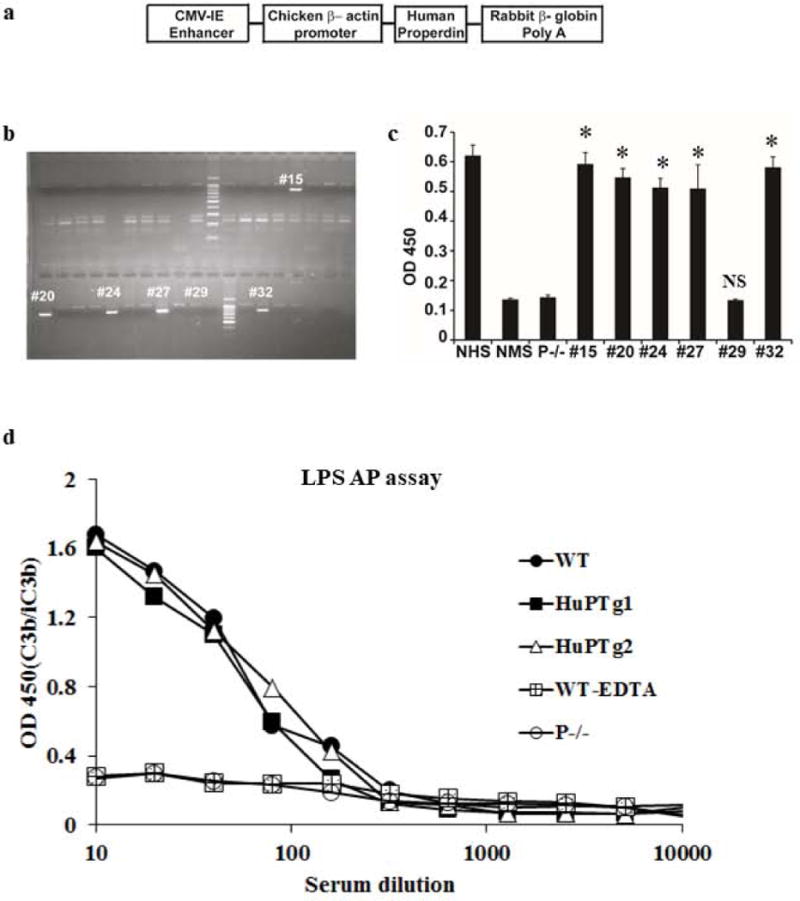
a. Human properdin cDNA construct used for transgenic mouse generation. The cDNA cassette is composed of the chicken β-actin promoter with CVM-IE enhancer, human P cDNA and the rabbit β -globin polyA tail for stable expression of the cDNA in eukaryotic cells. b. Genotyping of hP transgenic mice by PCR using hP-specific primers and tail DNA. Of 40 mice screened, five transgene-positive founders were identified by the presence of a PCR fragment of approximate 800 bp (#15, #20, #24, #27 and #32). c. Human P protein was detected by ELISA in the sera of the 5 transgene-positive mice but not in a transgene-negative mouse (#29). Normal mouse serum (NMS, i.e. serum from wild-type mouse) and serum from P−/− mouse were also negative for hP whereas normal human serum (NHS) was positive for hP. * p<0.0001, NS: non-significant. One-way ANOVA comparing with NMS or P−/− mouse serum. d. Transgenically expressed hP restored AP complement activity to P−/− mice. In contrast to P−/− mouse serum which showed no LPS-dependent AP complement activity, sera from two P−/− mice with hP transgene expression (HuPTg1 and HuPTg2) showed similar AP complement activity to that of a WT mouse. Data in panel c and d are representative of 2-3 independent experiments. Mean (SD) of triplicate assays (c) or average of duplicate assays (d) are shown.
