Figure 9. Schematic representation of the proposed actions of Pyk2 and estrogen on OBs.
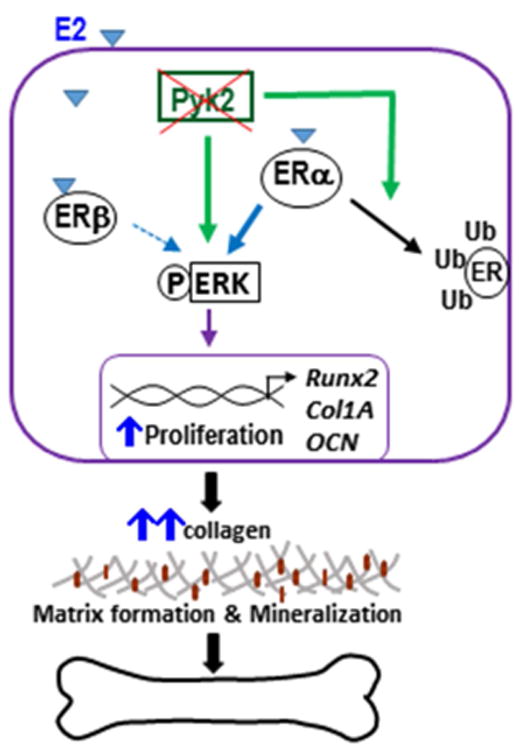
We postulate that inhibition of Pyk2 activity increases ERα degradation via the ubiquitin-proteosome pathway, which leads to an increase in ERK signaling and OB proliferation, and consequently promotes OB differentiation and mineralization activity. E2-stimulation, most likely acting through ERβ, has an additive effect on ERK signaling, which further promotes OB activity, leading to an increase in bone formation.
