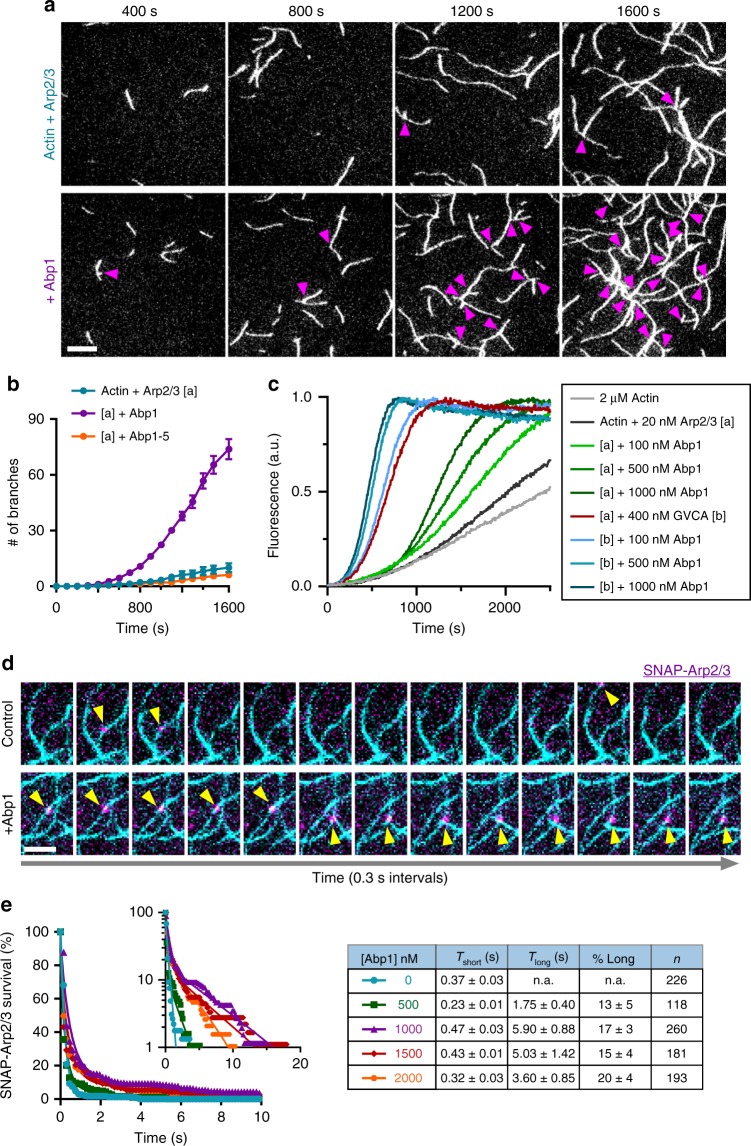
Fig. 1.
Abp1 stimulates Arp2/3-mediated nucleation of daughter branches. a Time points from representative TIRF microscopy actin assembly assays, with magenta arrows marking branch junctions. Reactions contain 1 µM actin (10% OG-labeled), 8 nM Arp2/3 complex ± 300 nM Abp1. Scale bar, 10 µm. b Kinetics of branch formation, quantified as the number of branches nucleated per FOV (18,000 µm2), averaged from 3 FOVs per reaction in each of two trials. Error bars, s.e.m. c Combined effects of Abp1 and GST-VCA on Arp2/3-mediated actin nucleation in pyrene actin assembly assays. Reactions contained 2 µM actin (10% pyrene labeled), 20 nM Arp2/3 complex, 400 nM GST-VCA (GVCA) and/or varying concentrations of Abp1, as indicated. d Montage showing association of JF646-SNAP-Arp2/3 complex molecules (10 nM, magenta) with anchored actin filaments (cyan), in the presence and absence of 1 µM Abp1, at 0.3 s intervals. Scale bar, 5 µm. e Cumulative survival curves (symbols) of JF646-SNAP-Arp2/3 molecules bound to actin filaments in the absence or presence of different concentrations of Abp1. Lines are fits to single exponential (absence of Abp1) or double exponential (presence of Abp1) distributions. Inset shows the same data, plotted on a log scale. Table includes number of binding events (n), fitted parameter values (Tshort, Tlong, and % long) with s.e. from n = 10,000 bootstraps samples