Figure 2.
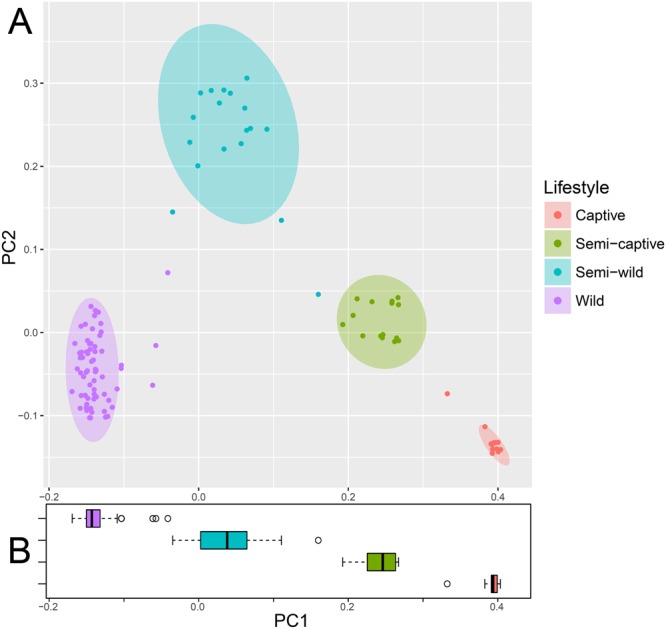
Principal coordinates plot showing (A) unweighted UniFrac ordination and (B) box plot of PC1 by population showing ecological distance between gut microbial communities in wild, semi-wild, semi-captive, and captive red-shanked doucs. All samples were obtained with the same protocol for V4 16S rRNA sequencing, and open-reference OTU picking was used. Douc microbiomes clearly clustered by population suggesting that each douc population had a unique microbiome, and thus were highly distinctive. Lifestyle has a major influence on gut microbial community structure, as doucs living under the most unnatural conditions (captive) had gut microbiomes most disparate from wild doucs (i.e., natural).
