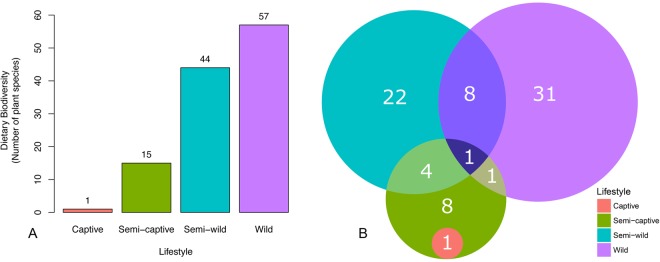
Figure 6.
Plant diversity in red-shanked douc diet reflects dietary diversity across populations. (A) Bar plots of dietary biodiversity, as measured by the number of plant species consumed by wild, semi-wild, semi-captive, and captive populations of red-shanked doucs. Wild doucs feed on 57 different plant species, whereas the semi-wild doucs feed on 44 different plant species annually61,113. In contrast to the high dietary diversity consumed by the wild and semi-wild doucs, semi-captive and captive doucs are fed far fewer plant species. Specifically, semi-captive doucs are feed on approximately 15 plant species and the captive doucs are fed a single plant species113. Fruits and vegetables consumed by semi-captive and captive doucs were not a component of the “plant species” dietary category referred to in the Fig. 6. (B) Venn diagram depicting the number of plant genera consumed by the wild, semi-wild, semi-captive, and captive douc populations, while the numbers in overlaps representing the genera eaten by the constituent populations. Number of genera for the wild population was obtained from Clayton (unpublished). Number of genera for the semi-wild population was obtained from a combination of Clayton (unpublished) and Otto61.