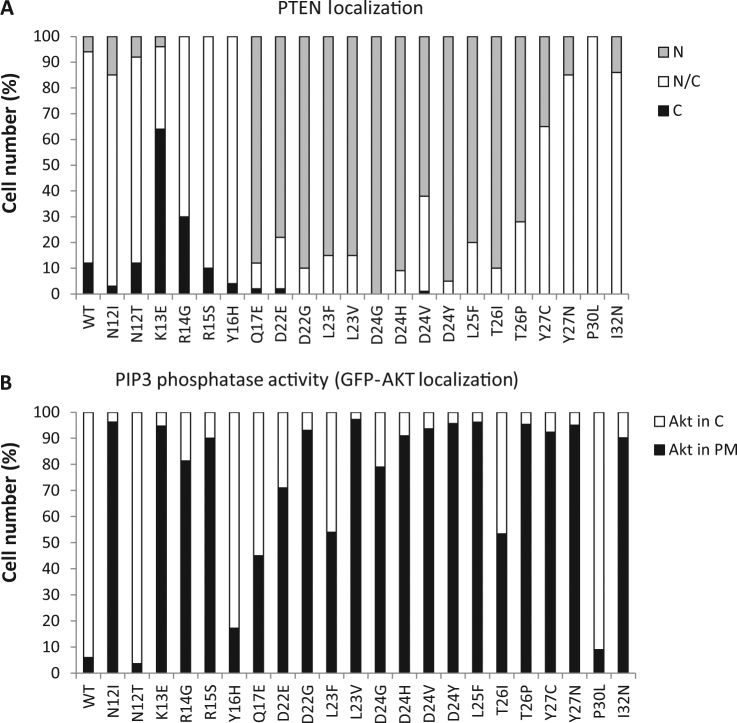
Fig. 5.
Functional analysis of PTEN N-terminal germline mutations. a COS-7 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding the indicated PTEN mutations (WT, wild type), in the background of PTEN-GFP, and cells were analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. Quantification of percentages of cells with nuclear (N), cytoplasmic (C), or nuclear/cytoplasmic (N/C) localization is shown. b In vivo PTEN activity in the yeast heterologous model. Yeast cells were co-transformed with plasmids encoding p110α-CAAX, GFP-AKT1, and the indicated PTEN variants (WT, wild type), and PIP3-phosphatase activity was assessed as in Fig. 2. The percentage of cells with GFP-AKT1 in the cytoplasm (C), indicative of PTEN PIP3-phosphatase activity, or in the plasma membrane (PM), within the population of transformant clones co-expressing p110α-CAAX, GFP-AKT1 and the respective PTEN variants, is represented. Data are the average of three experiments on three different clones (n ≥ 100 cells per clone)