Figure 1.
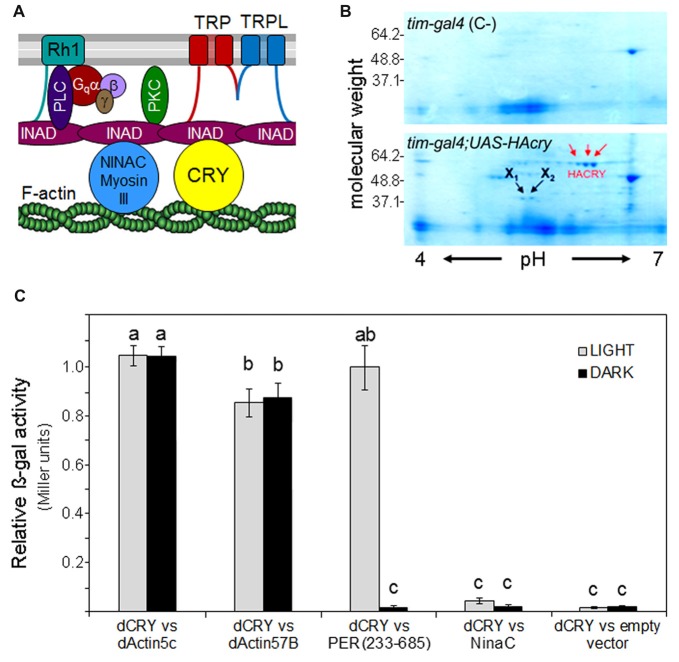
Cryptochrome (CRY) interacts with F-Actin. (A) Putative position of CRY in the phototransduction cascade of the fly rhabdomere. The cartoon is modified after Montell (2012). INAD (Inactivation No AfterpotentialD) is a crucial PDZ-scaffold protein which gathers together many components of the cascade. It is connected to F-actin via the MyosinIII protein NINAC as well as via CRY (according to the present results). In addition, INAD interacts with rhodopsin 1 (Rh1), the transient-receptor-potential channels TRP and TRPL, Phospholipase C (PLC) and Phosphokinase C (PKC). (B) Coomassie blue-stained 2D gel of head protein extracts co-immunoprecipitated with an anti-HA antibody. HACRY overexpressing flies (yw;tim-gal4/+;uas-HAcry/+) and relative control (yw;tim-gal4 (C-)) have been reared in 12:12 LD and collected in the dark (ZT24). Protein complexes have been subjected to 2D separation (1st dimension: IPG STRIP pH 4–7; 2nd dimension NuPage ZOOM gel 4%–12% Invitrogen). Red arrows indicate the spots relative to HACRY, while X1 and X2 are spots corresponding to putative HACRY partners. (C) Yeast two-hybrid assays showing the light-independent interaction between dCRY and dAct-5C and dAct-57B. A fragment of PER (aa 233–685), known to interact with dCRY in a light-dependent manner, and NinaC were used as positive and negative control of the interaction, respectively. The activity of the empty prey vector is considered as background. Reported is the β-galactosidase activity (Miller units) normalized to the activity of PER(233–685) in light. Mean ± SEM of seven independent clones, analyzed in triplicates, is shown. For the controls and for the “empty vector”, three clones were tested. Statistics: one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Significantly different values are marked with different letters.