Figure 1.
Bound Lipids Affect the Oligomerization of UapAG411VΔ1-11
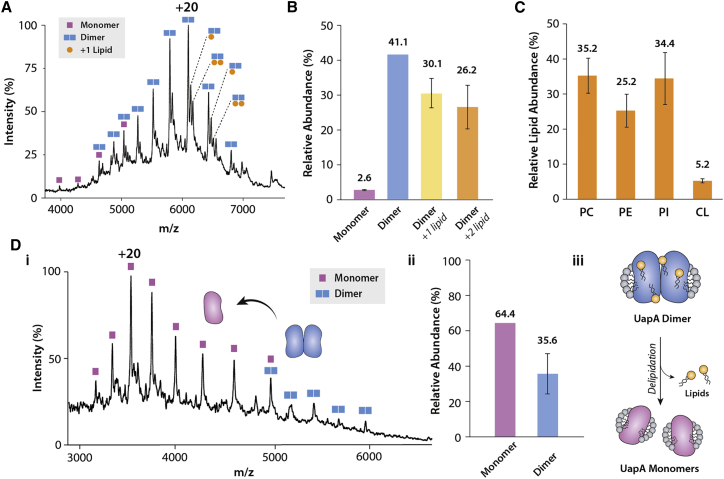
(A and B) Mass spectrum of UapAG411VΔ1-11 (A) highlighting the presence of both monomer and dimer species and lipid binding to the dimer. (B) Relative abundance of the different forms of UapAG411VΔ1-11 identified by native MS.
(C) Relative abundance of each lipid class identified by LC-MS and LC-MS/MS from the lipid extract of a purified UapAG411VΔ1-11 sample. PC, phosphatidylcholine; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PI, phosphatidylinositol; CL, cardiolipin.
(D) (i) Mass spectrum showing the effect of delipidation on the oligomerization of UapAG411VΔ1-11. (ii) The relative abundance of monomer and dimer in the delipidated sample. (iii) Schematic summarizing the effects of delipidation. Removal of lipid causes dissociation of the UapAG411VΔ1-11 dimer into monomers.
The relative abundance of each oligomeric species in (B), (C), and (Dii) was quantified using UniDec software (Marty et al., 2015). The mass spectra are representative of three independent experiments carried out under identical conditions. The relative abundance data are the average ± SD (n = 3) and the average values are given above the bars on each chart.