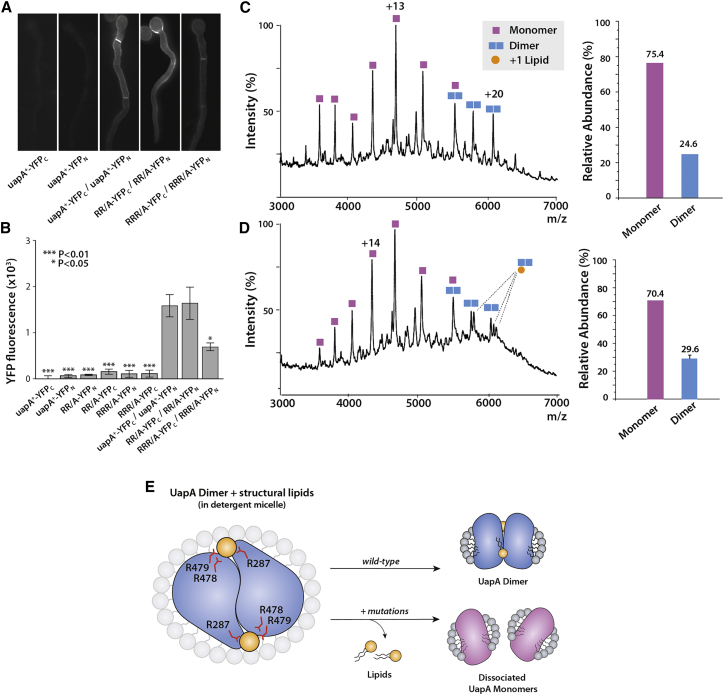
Figure 5.
The R287A/R478A/R479A UapA Mutant Reduces Dimer Formation
(A) Bimolecular complementation (BiFC) analysis of the R478A/R479A (RR/A) UapA mutant and the R287A/R478A/R479A (RRR/A) UapA mutant. Mutant constructs tagged with the individual YFP domains were co-expressed in A. nidulans. Upon UapA dimerization the YFP is reconstituted. YFP fluorescence was measured by epifluorescence inverted microscopy. WT UapA (uapA+) expressed individually with either the C-terminal domain of YFP (YFPC) or the N-terminal domain of YFP (YFPN) is the negative control.
(B) Relative quantification of plasma membrane fluorescence intensity of mutants compared with WT UapA +/− YFPC/UapA +/− YFPN.
(C) (Left) Mass spectrum of UapA RRR/A with a G411V mutation and 11-residue N-terminal truncation. (Right) Relative abundances of each oligomer of UapA RRR/A + G411VΔ1-11.
(D) (Left) Mass spectrum of UapA RRR/A + G411VΔ1-11 with PI (34:1) added at a ratio of 1:100 protein/lipid. (Right) Relative abundances of each oligomer of RRR/A + G411VΔ1-11 with PI (34:1) added at a ratio of 1:100 protein/lipid. See Figure 1A for the relative abundances of each oligomer of UapAG411VD1-11 under identical conditions. The relative abundance of each species was quantified using UniDec software (Marty et al., 2015). The mass spectrum is representative of three independent experiments carried out under identical conditions. The relative abundance data are the average ± SD, n = 3.
(E) Schematic showing the effect of the R287/R479/R478 mutations on lipid stabilization of the UapA dimer. Mutations of R287A/R478A/R479A abolish lipid binding capability, resulting in the dissociation of UapA into monomers.