Figure 2.
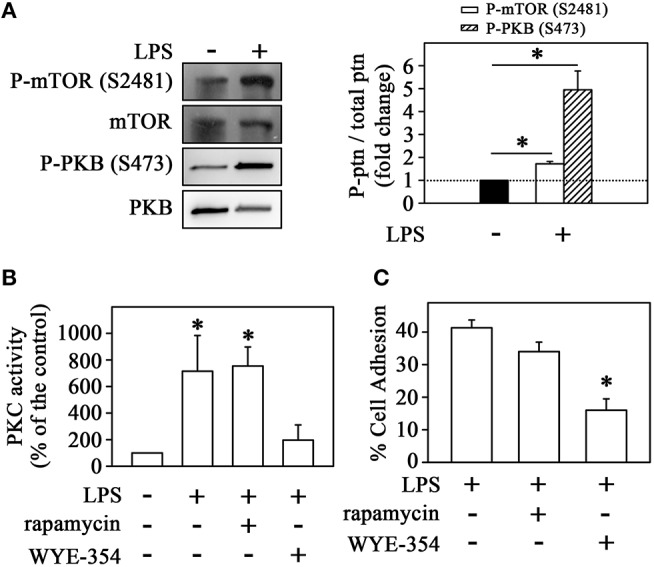
LPS induces the mTORC2/PKC pathway in monocytes. (A) The effect of LPS on mTOR and PKB phosphorylation at residues S2481 and S473, respectively (n = 3) (left panels). The levels of phosphorylation were determined by the relationship between the optical density of the specific phosphorylated residue and the total fraction. The result is expressed in fold change in relation to an untreated control (bar graph). Images are representative of three independent experiments. The effect of 10−9 M rapamycin and 10−6 M WYE-354 on (B) PKC activity and (C) THP-1 cell adhesion induced by LPS (n = 3). mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; Akt/PKB, protein kinase B. The results are presented as means ± SE. *p < 0.05 vs. unstimulated non-adhered cells (control).
