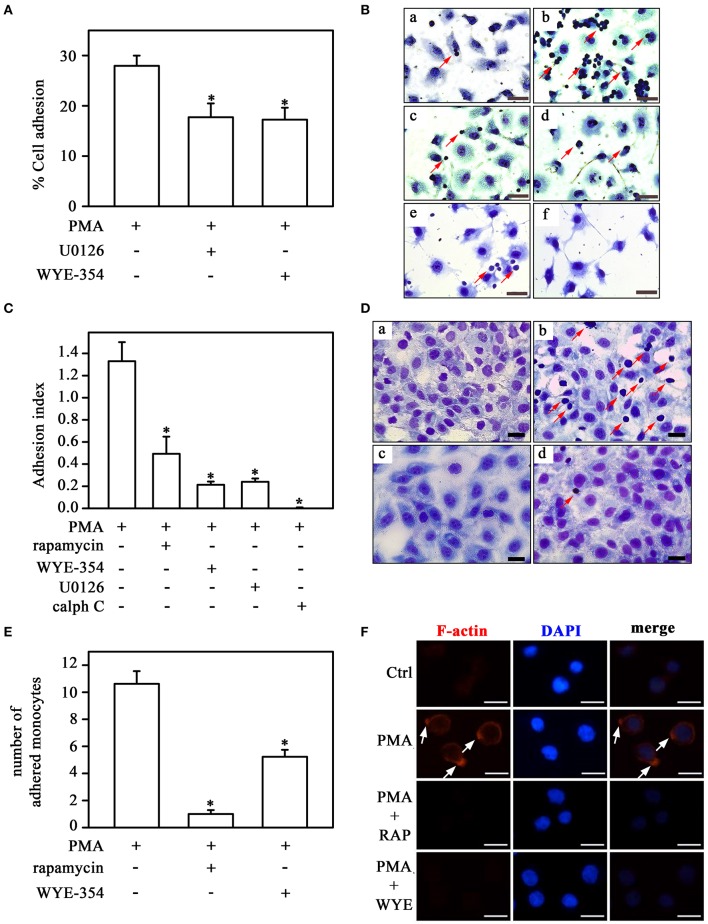
Figure 9.
Direct activation of PKC on monocyte adhesion involves the mTORC1/S6K pathway. (A) The effect of U0126 and WYE-354 on PMA-induced THP-1 cell adhesion (n = 3). (B,C) Effects of rapamycin, WYE-354, U0126, and calphostin C on PMA-induced THP-1 cell adhesion under static conditions. (D,E) Effects of rapamycin and WYE-354 on PMA-induced THP-1 cell adhesion under flow conditions. (B,D) Images are representative of the experiments. a, control; b, LPS; c, LPS+rapamycin; d, LPS+WYE-354; e, LPS+U0126; f, LPS+calph C. Red arrows indicate adhered monocytes. Scale bar, 50 μm. (C,E) Quantification analyses. (F) Effect of rapamycin and WYE-354 on PMA-induced THP-1 cells on cytoskeleton rearrangement as described in Figure 5. (a–c) control, (d–f) PMA treatment, (g–i) PMA and rapamycin treatment, (j–l) PMA and WYE-354 treatment. Cells were examined by microscopy with 40 × objective. Scale bar, 10 μm (n = 3). Calph C, calphostin C; RAP, rapamycin; WYE, WYE-354. The results are presented as means ± SE. *p < 0.05 vs. PMA.