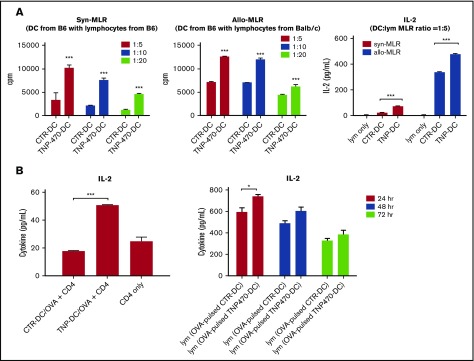
Figure 2.
TNP-470–treated DCs induce T-cell activation in vitro and in vivo. (A) BMDCs were cultured with syngeneic (left) and allogenic (middle) lymphocytes at different ratios (1:5, 1:10, 1:20) for 72 hours (syngeneic culture) and 48 hours (allogenic culture). 3H-labeled thymidine (0.5 μCi/well) was added in the last 16 hours of culture and cell proliferation was measured by incorporated 3H-labeled thymidine. Data presented as mean ± SEM from 3 independent experiment. ***P < .001 TNP-DC coculture vs CTR-DC coculture. Culture supernatant from 72-hour syngeneic culture and 48-hour allogenic culture (DC:T-cell ratio = 1:5) were harvested and detected for IL-2 secretion (right). ***P < .001 TNP-DC coculture vs CTR-DC coculture. Data presented as mean ± SEM from 3 independent experiment. (B) Activation of in vitro OVA-specific CD4 T cells. CD4 cells from OVA-immunized mice were collected and cultured with TNP-470/vehicle- treated and OVA-pulsed DCs for 24 hours. Culture supernatant was detected for IL-2 secretion (left). ***P < .001 OVA-pulsed CTR-DC coculture vs OVA-pulsed TNP-DC coculture. Data presented as mean ± SEM from 3 independent experiment. Activation of OVA-specific lymphocytes in vivo. C57BL mice were immunized with OVA-pulsed DCs (TNP-470/vehicle-treated). Lymphocytes from mice in different groups were harvested and stimulated with OVA ex vivo. Culture supernatant from 24-, 48-, and 72-hour culture was detected for IL-2 secretion (right). *P < .05 lymphocytes from mice immunized with OVA-pulsed TNP-DC vs OVA-pulsed CTR-DC counterpart. Data presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD) from 3 independent experiment.