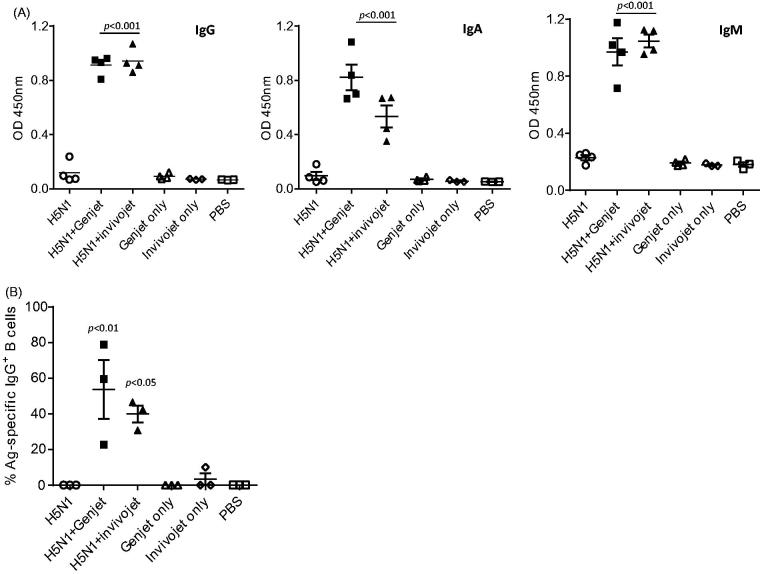
Figure 1.
GenJet™ and in vivo-jetPEI enhances the H5N1 vaccine-induced systemic antibody responses and memory B-cell responses. Balb/c mice (5 mice/group) were intranasally administered with 3 µg of A/IN/05 vaccine with or without GenJet™ (10 µl/each mouse as described in previous study (Kulkarni et al., 2014)) or in vivo-jetPEI® (0.6 μl/mouse according to manufacturer’s protocol). One month later, mice were boosted with the same vaccine formulations. The control mouse group received GenJet™, in vivo-jetPEI® or PBS at both time points. (A) Three weeks after booster immunization, sera were collected and IgG, IgA and IgM antibodies against A/IN/05 were assessed by ELISA. (B) One week after booster immunization, the spleen were harvested and the frequency of A/IN/05-specific IgG+ ASCs in the spleen were measured by ELISPOT assay. The number of A/IN/05-specific IgG+ ASCs were normalized against the number of total IgG+ secreting ASCs and presented as % Ag-specific IgG+ B cells. The data are representative of two independent experiments (3–5 mice each group) and error bars represent SEM. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-analysis was used to analyze differences among different groups. p < .05, p < .01 and p < .001 as compared to the H5N1 vaccine alone group.