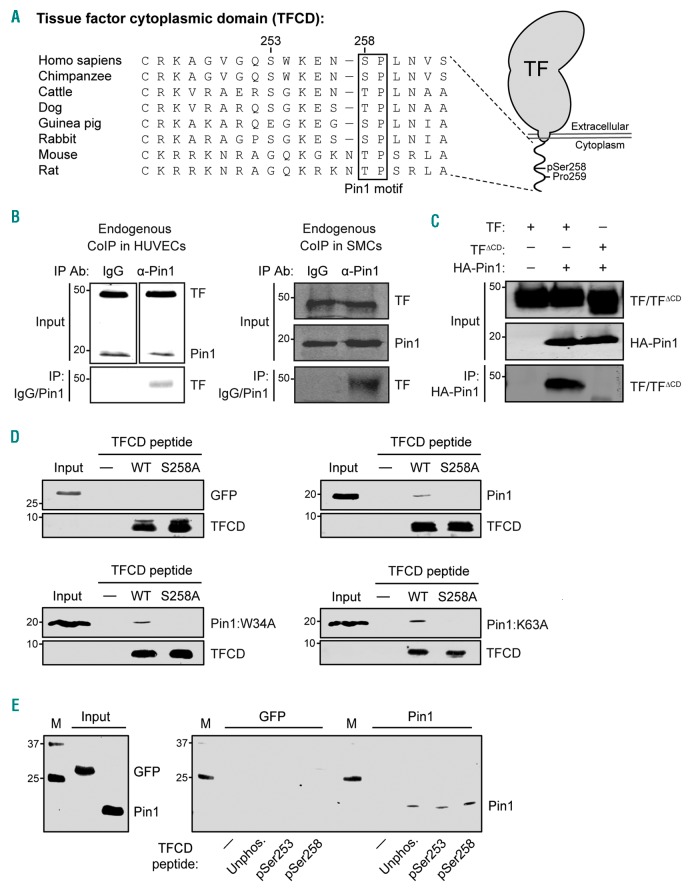
Figure 2.
Pin1 interacts with Tissue Factor (TF) via the twenty-amino acid cytoplasmic domain (TFCD). (A) Amino acid sequence similarity of the TFCD in different species, showing strong conservation of the Pin1 recognition motif Ser/Thr-Pro (box). (B) Co-immunoprecipitation (CoIP) for TF and Pin1 in human PMA-stimulated HUVECs or smooth muscle cells (SMC) with control IgG or anti-Pin1 antibody (IP: IgG/Pin1) and analyzed by western blot with anti-TF antibody. Input TF and Pin1 levels are also shown. (C) CoIP for TF and Pin1 in HEK293T whole cell lysates over-expressing HA-tagged Pin1 and either full-length TF or TFΔCD using anti-HA antibody (IP: HA-Pin1) analyzed by western blot with anti-TF antibody. Input TF/TFΔCD and HA-Pin1 levels are also shown. (D) Pull-down assay with biotinylated peptides encoding wild-type human TFCD (WT) or TFCD with an S258A mutation. Full-length Pin1, Pin1 mutants with a disrupted WW-domain (Pin1:W34A) or lacking isomerase activity (Pin1:K63A), or GFP (as a negative control) were detected by western blot. (E) Pull-down assay with cysteine-linked TFCD-encoding peptides that were unphosphorylated or phosphorylated at either Ser253 or Ser258. Full-length Pin1 and GFP (as a negative control) were detected by western blot.