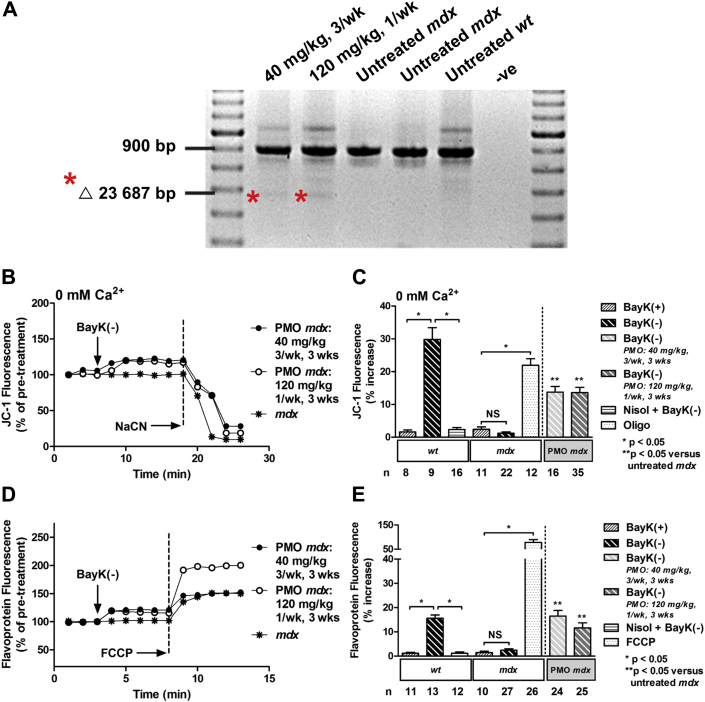
Figure 1.
Short-Term, High-Dose Treatment of 4- to 5-Day-Old mdx Mice With PMO Results in Exon Skipping of Dystrophin, and Partial Restoration of Ψm and Flavoprotein Oxidation in Response to Activation of ICa-L
(A) Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction on cardiac ribonucleic acid from phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer (PMO)-treated murine model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (mdx) mice demonstrating exon 23 skipping (Δ 23 687 base pairs [bp]), as indicated by asterisks, and untreated mdx and wild-type (wt) control mice. (B) Representative ratiometric 5,5',6,6'-tetrachloro-1,1',3,3'-tetraethylbenzimidazolylcarbocyanine iodide (JC-1) fluorescence recorded in myocytes from PMO-treated mdx mice, and an untreated mdx mouse before and after exposure to 10 μM BayK(–) under calcium-free conditions (0 mM Ca2+). (C) Mean ± SEM of JC-1 fluorescence for all myocytes exposed to drugs as indicated. (D) Representative traces of flavoprotein fluorescence recorded in myocytes from PMO-treated mdx mice and an untreated mdx mouse before and after exposure to 10 μM BayK(–). (E) Mean ± SEM of flavoprotein fluorescence for all myocytes exposed to drugs as indicated. PMO treatments: 40 mg/kg (3×/week) or 120 mg/kg (1×/week) for 3 weeks. BayK(+) = 10 μM; FCCP = 50 μM carbonyl cyanide-4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenylhydrazone; ICa-L = L-type Ca2+ channel; NaCN = 40 mM sodium cyanide; Nisol = 15 μM nisoldipine; NS = not significant; Oligo, 20 μM oligomycin; -ve = negative control; Ψm, mitochondrial membrane potential.