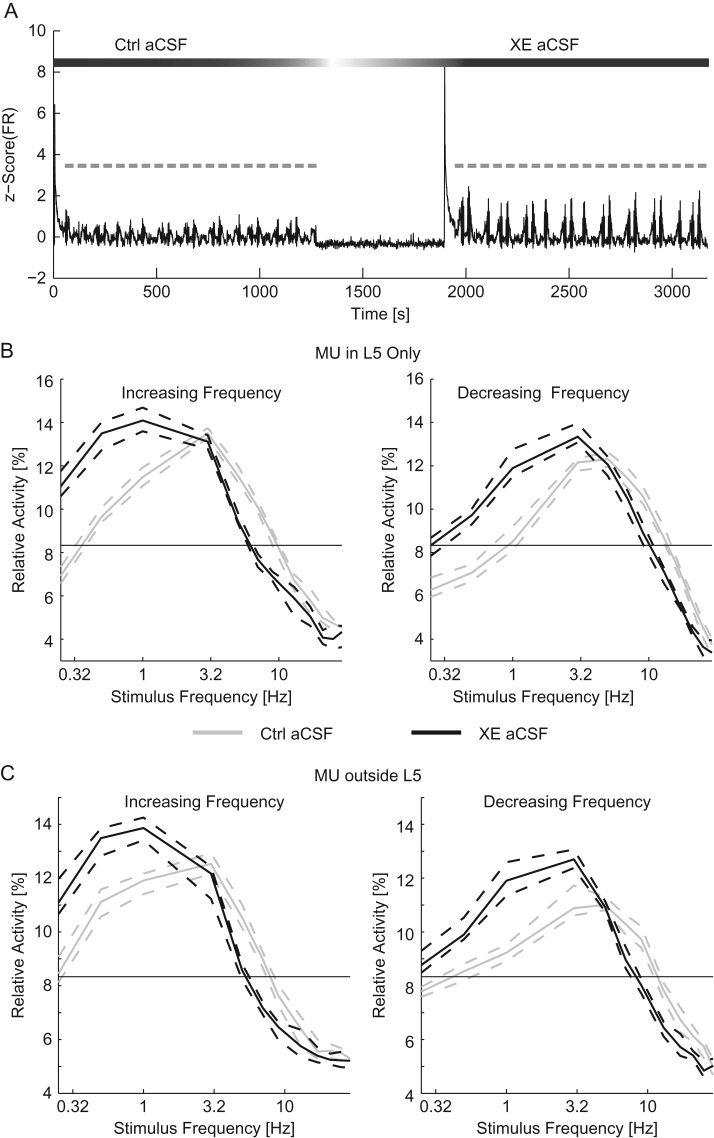
Figure 4.
Addition of XE-991 reduced the resonant frequency of networks. (A) The z-scored time course of the MU firing rate (black). Chirp trials are indicated in gray. After the first epoch of stimulation, the perfusion was switched to XE aCSF. Ten minutes after the application of XE aCSF, a second epoch of stimulation was applied. (B) The relative activity for each frequency of stimulation for increasing (left) and decreasing (right) frequency chirps for MU recorded within L5. (C) The relative activity for MU recorded outside of L5 for increasing (left) and decreasing (right) frequency chirp stimuli. For (B) and (C), response to optogenetic chirps in control aCSF is in gray while the response to chirps delivered in XE aCSF is in black. The thin black line indicates chance activity levels. With XE-991 in the bath, the response to low-frequency stimuli was increased. Ctrl aCSF, control aCSF. Dashed lines indicate the 95% confidence interval of the median.