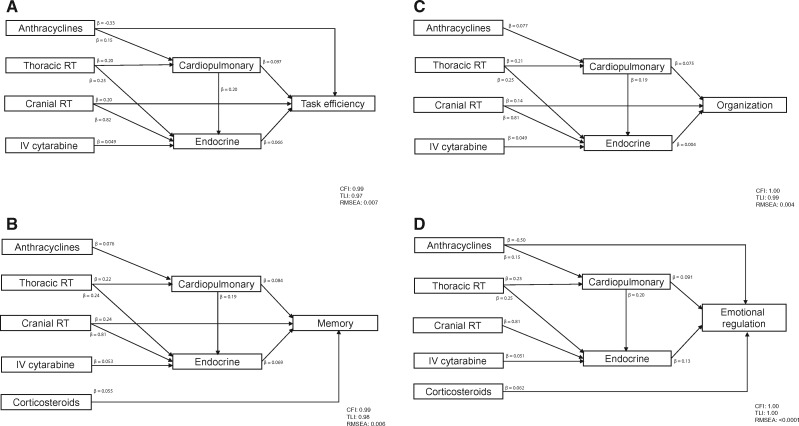
Figure 2.
Pathways of cancer therapy on neurocognitive outcomes. Final path models are presented for each neurocognitive measure. All models are adjusted for sex, time since diagnosis, and age at diagnosis. Model fit indices are represented by comparative fit index, Tucker Lewis Index, and root mean square error of approximation. A) The path model for task efficiency. The impact of cranial radiotherapy (RT) on task efficiency is modified by sex (P = .002) and age at diagnosis (P < .001). The impact of anthracyclines on task efficiency is modified by time since diagnosis (P = .03). The impact of thoracic RT on endocrine disease is modified by age at diagnosis (P = .001). The impact of cranial RT on endocrine disease is modified by sex (P = .01), time since diagnosis (P < .001), and age at diagnosis (P < .001). B) Figure 2B shows the path model for memory. The impact of thoracic RT on endocrine disease is modified by age at diagnosis (P = .001). The impact of cranial RT on endocrine disease is modified by sex (P = .003), time since diagnosis (P < .001), and age at diagnosis (P < .001). C) The path model for organization. The impact of thoracic RT on endocrine disease is modified by age at diagnosis (P = .001). The impact of cranial RT on endocrine disease is modified by sex (P = .002), time since diagnosis (P < .001), and age at diagnosis (P < .001). D) The path model for emotional regulation. The impact of anthracyclines on emotional regulation is modified by time since diagnosis (P = .002). The impact of thoracic RT on endocrine disease is modified by age at diagnosis (P = .001). The impact of cranial RT on endocrine disease is modified by sex (P = .004), time since diagnosis (P < .001), and age at diagnosis (P < .001). P values are derived from a probit model with a robust weighted least squares estimator (WLSMV). All P values are two-sided. CFI = comparative fit index; IV = intravenous; RMSEA = root mean square error of approximation; RT = radiation therapy; TLI = Tucker Lewis Index.