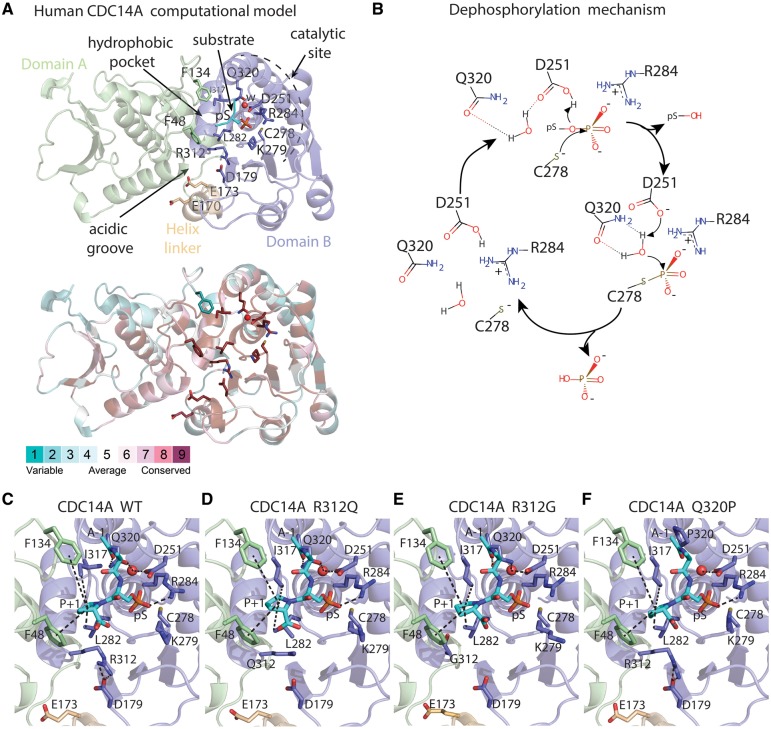
Figure 2.
Molecular model of human CDC14A wild-type (WT) and three missense variants constructed using as template the x-ray structure of human CDC14B, a paralogue of CDC14A. (A) Domains A (green) and B (light-purple), helix linker (yellow) and a phosphorylated peptide (substrate, cyan). The phosphorylated serine (pS) is proximal to a water molecule (w, red sphere) responsible for phosphate hydrolysis. Lower panel show evolutionary conservation of the residues. (B) Reaction mechanism for CDC14-mediated dephosphorylation of phosphoprotein substrates with its phosphate group oriented on top of the positive dipole of helix 4B, where the core enzyme machinery is located. (C–F) Catalytic sites in the structural models of the human CDC14A WT and substitutions p.R312Q, p.R312G and p.Q320P. The substrate is shown as cyan sticks where alanine and proline are indicated as A-1 and P + 1. Interactions involving the catalytic site residues are indicated by dashes.