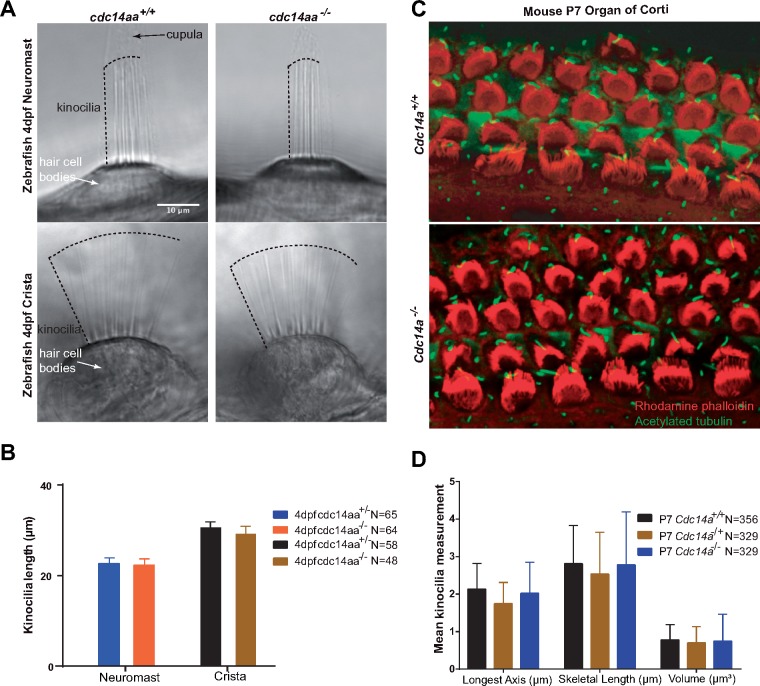
Figure 6.
Kinocilia of hair cells in mouse organ of Corti and zebrafish neuromast and posterior crista from homozygous mutants are indistinguishable in length from wild-type. (A) Zebrafish 4 days post-fertilization (4 dpf) showing representative images of kinocilia for live-anesthetized heterozygous and homozygous mutant cdc14aa. (B) A total of 112 kinocilia (64 neuromast and 48 crista) from homozygous mutants and 123 (65 and 58) kinocilia from heterozygotes were measured. Two neuromasts and one crista examined per fish and 5 homozygous mutants and 5 heterozygotes zebrafish larvae were analyzed. Statistical analyses of mean kinocilia lengths of heterozygotes and homozygous mutant larvae show no significant difference. See Supplementary Material, Figure S9E and F for individual data points and statistical analyses. Error bars are standard deviations. (C) Representative images of P7 mouse organ of Corti from a wild-type and Cdc14atm1b/tm1b homozygous mutant mouse stained with rhodamine phalloidin (red) and acetylated tubulin (green). Lengths of kinocilia from two ears (Cdc14atm1d/tm1d) were measured using Volocity software to correct for parallax. (D) Kinocilia lengths (m) of wild-type and Cdc14atm1d/tm1d are not significantly different. Error bars are standard deviations. N is the number of hair cells examined.