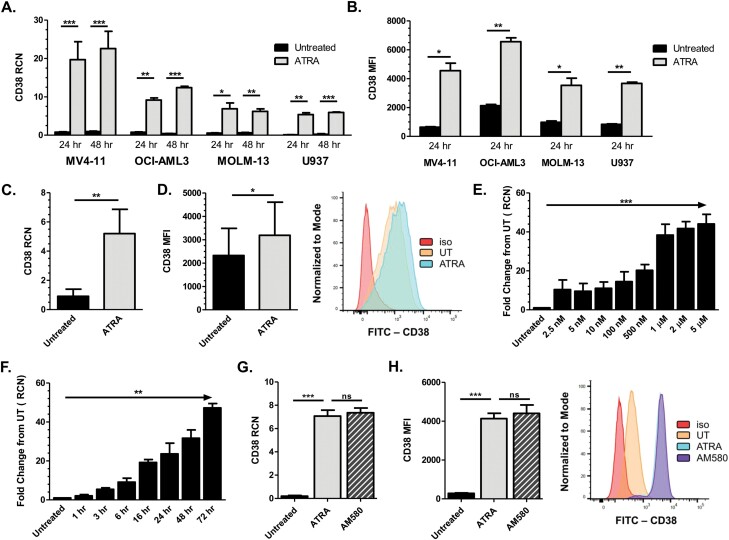
Fig. 1.
ATRA up-regulates CD38 in AML cells. (A) MV4-11 (n = 5 separate experiments), OCI-AML3, MOLM-13 and U937 cells (n = 3 separate experiments each) were treated with 1 µM ATRA for 24 and 48 h (ATRA added every 24 h). CD38 transcript was measured by qPCR. (B) AML cell lines MV4-11, OCI-AML3, MOLM-13 and U937 (n = 3 separate experiments each) were treated with 1 µM ATRA for 24 h and analyzed for CD38 surface protein expression by flow cytometry. (C, D) Primary AML patient apheresis samples were treated with 1 µM ATRA for 24 h and CD38 transcript level (C; n = 10 donors) and surface protein expression (D; n = 9 donors) were measured; representative histogram for the flow cytometry is shown in (D). (E) MV4-11 cells (n = 3 separate experiments) were treated with concentrations of ATRA ranging from 0 to 5 µM and CD38 transcripts were measured after 24 h by qPCR. (F) MV4-11 cells (n = 3 separate experiments) were treated with 1 µM ATRA for 1–72 h and CD38 transcripts were measured by qPCR. (G, H) MV4-11 cells (n = 3 separate experiments) were treated with 10 nM ATRA or AM580 for 24 h; CD38 levels were measured by qPCR (G) and flow cytometry (H; representative histogram shown). *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001.