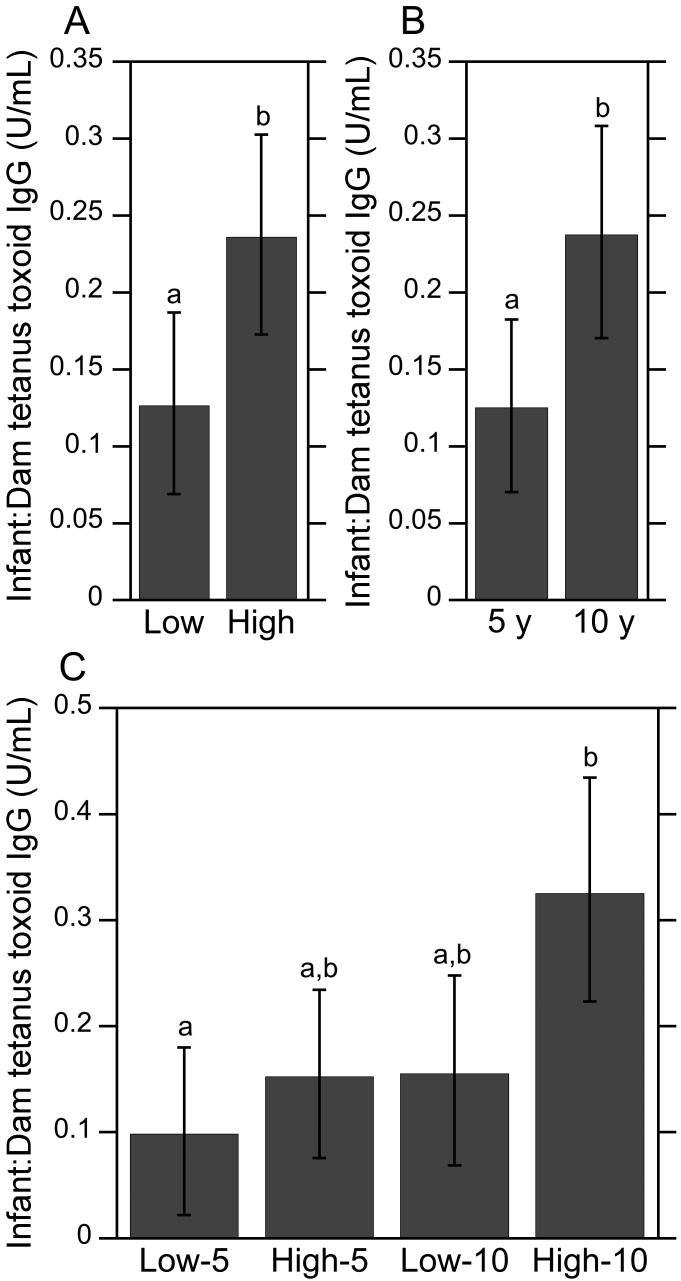
Figure 4.
Infant-to-dam ratio of antitetanus IgG levels. (A) The ratio of infant-to-dam TT IgG levels were significantly lower among low-ranking infant and maternal pairs than that observed for their more dominant counterparts. (B) The mean ratio of antitetanus IgG levels among infant and maternal pairs 5 y after immunization was significantly lower than those 10 y afterward, regardless of social rank. (C) Analyses of the same data by 4 experimental group revealed that the mean ratio of infant-to-dam TT IgG levels was significantly higher among high-ranking infant and maternal pairs at 10-y after immunization compared with lower-ranking animals at 5 y afterward. Nearly significant group differences were found when comparing low-10 with high-10 (P = 0.07) and high-5 with high-10 (P = 0.0501). Different letters indicate significantly (P < 0.05) different values. Data are expressed as means ± 95% confidence intervals.