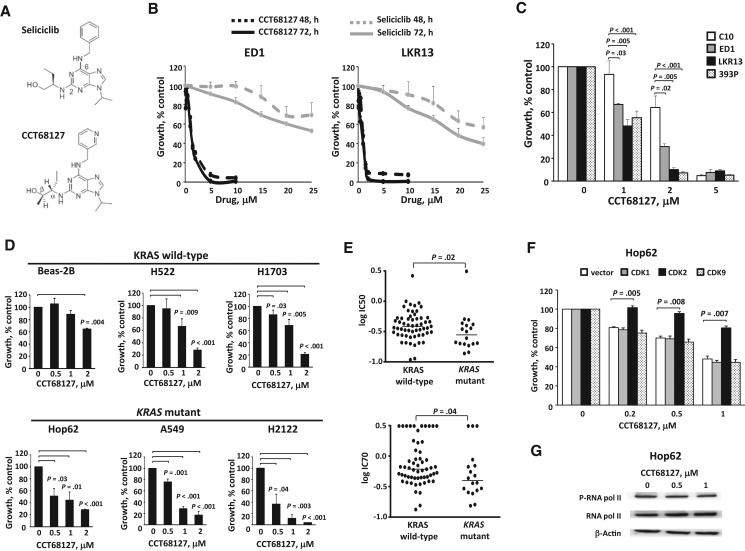
Figure 1.
Antiproliferative effects of CCT68127 against murine and human lung cancer cells. A) Structures of seliciclib and CCT68127. B) Dose-response treatments of seliciclib vs CCT68127 in murine (ED1 and LKR13) lung cancer cells. C) CCT68127 effects on growth of murine immortalized pulmonary epithelial cells (C10) and lung cancer cells (ED1, LKR13, and 393P). D) Effects of CCT68127 on growth of human immortalized bronchial epithelial (Beas-2B) and lung cancer (H522, H1703, Hop62, A549, and H2122) cells. E) Comparison of growth inhibition of CCT68127 in KRAS wild-type vs mutant lung cancer cells using a high-throughput screen of 75 human lung cancer cells. Each symbol displays an individual cell line. Bars represent median values. F) Consequences of engineered gain of individual CDK species expression on proliferation of CCT68127-treated Hop62 human lung cancer cells. G) Immunoblot analyses of phosphorylation of RNA polymerase II in Hop62 human lung cancer cells following CCT68127 treatment. Error bars are standard deviation. The P values were computed using t test with multiple comparison adjustment by Tukey's method (C and F) and Dunnett's method (D), and Mann-Whitney U test (E). All statistical tests were two-sided.