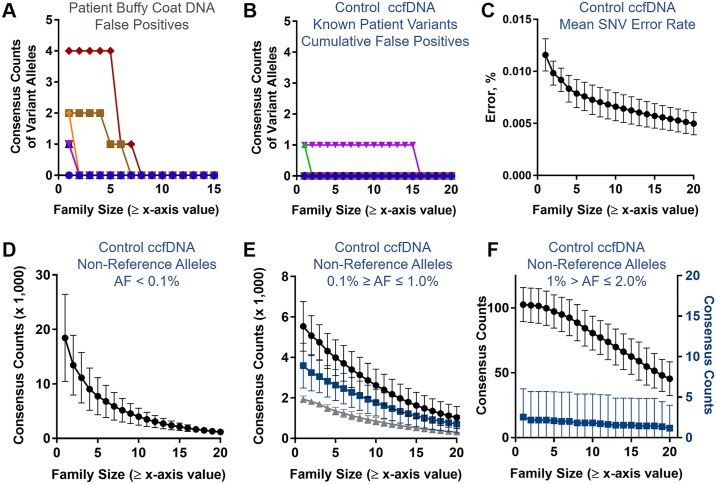
Fig 5. Reduction of false positives at larger family sizes.
Corresponding variants present in patient ccfDNA were queried in matched buffy coat DNA (A). False positives were few and incrementally decreased with larger family sizes (A). In (B), the cumulative number of false positives from all healthy control ccfDNA and all five targeted patient variants is shown. Overall, only two false positives were identified. In (C), the mean error rate across the entire capture panel (128 genes, 128 kb) decreased with increasingly larger family sizes. Total consensus aligned counts for non-reference alleles with AF < 0.1% (D), 0.1% ≥ AF ≤ 1.0% (E), and 1.0% > AF ≤ 2.0% (F) are shown (black circles). In (E) and (F), non-reference alleles are sub-categorized as “unique” (blue squares) or “shared” (gray triangles). In (F), “shared” non-reference alleles are not shown as they are similar to the total count. In (F), the “unique” non-reference allele count is plotted on a second y-axis. In (C-F), whiskers correspond to the standard deviation.