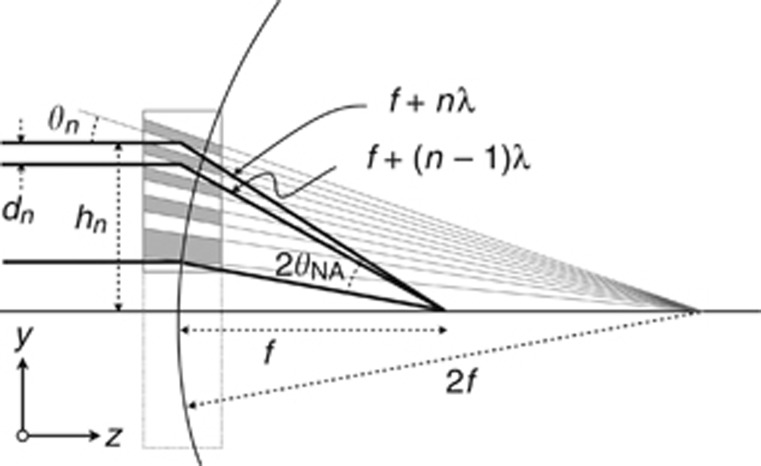
Figure 1.
To achieve high diffraction efficiency across the entire pupil of a multilayer Laue lens, the layer periods dn at heights hn must follow the zone plate law such that reflected rays constructively interfere at the focus. The layers must be wedged so that Bragg’s law sin θn=λ/(2dn) is satisfied locally at every bi-layer for a wavelength λ. For a lens of focal length f, this places the layers normal to a circle of radius 2f. The lens can be thought of as an off-axis portion of a larger parent lens. The numerical aperture is given by sin θNA, where θNA is half of the difference between the largest and smallest deflection angles.