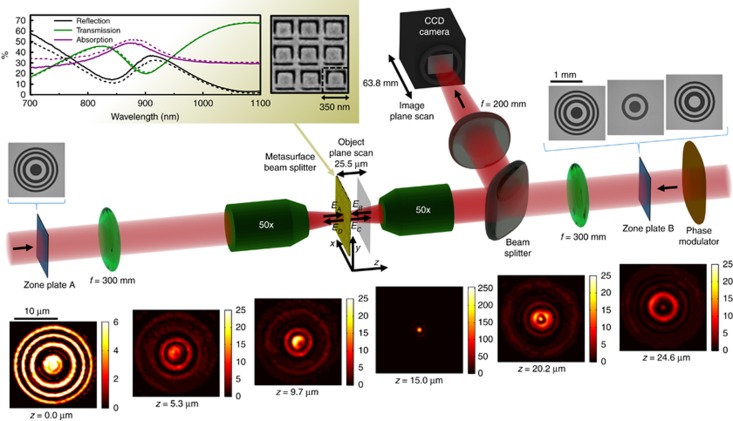
Figure 2.
Coherent control of optical focusing is achieved by imaging Fresnel zone plates A and B onto opposite sides of a metasurface beam splitter using coherent light of 790 nm wavelength. At the metasurface, the images of the Fresnel zone plates A and B are demagnified 75 × by a combination of a 300-mm focal length lens and an infinity-corrected 4-mm focal length 50 × objective. Using the same objective combined with a 200-mm focal length lens, the field structure at different distances z from the metasurface is imaged onto a CCD camera by translating the camera along the optical path. The image sequence at the bottom shows intensity patterns recorded by the camera at different distances z when identical zone plates A and B are simultaneously imaged on either side of the lossy metasurface positioned near a node of the standing wave (φ=0) as in the third row of Figure 3. Here the intensity map taken at z=15 μm depicts the focal hotspot created by the Fresnel zone plates. The upper left inset shows a scanning electron micrograph of part of the metasurface alongside its traveling wave transmission, reflection and absorption spectra (where solid and dotted lines show measurements for opposite illumination directions). See Supplementary Fig. S1 for an enlarged unit cell with dimensions.