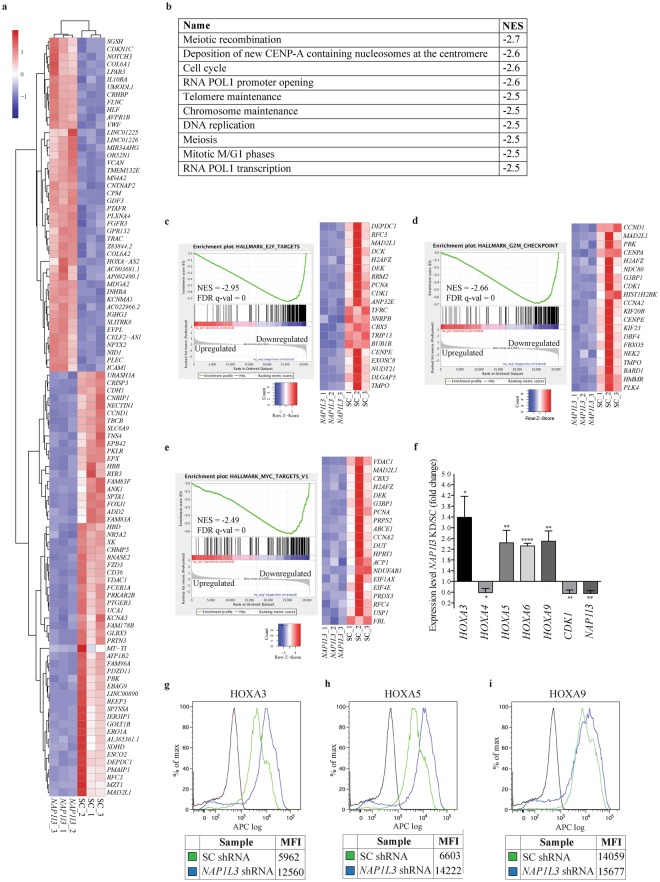
Figure 6.
NAP1L3 downregulation in cord blood cells induces an expression profile linked to cell cycle progression. (a) Heatmap of the top 100 genes differentially expressed in (Lin−CD34+CD38−) UCB HSCs transduced with shRNA vectors against NAP1L3, relative to a control vector, 72 hours post transduction. Up regulated genes are shown in red and down regulated genes are shown in blue. The data represents clustering of the individual experiments, n = 3. (b) List of the ten most significant correlations between the predefined MSigDB GO Biocarta gene set pathways and the gene expression changes resulting from shRNA-based downregulation of NAP1L3, relative to UCB HSCs transduced with negative control vectors. Normalised enrichment score (NES) for each pathway is shown in the right column. (c–e) Enrichment plots of gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) of gene expression profiling changes in response to NAP1L3 knockdown in UCBs, demonstrating significant negative correlations with E2F targets (c), G2/M checkpoint (d) and MYC targets (e). The bar charts represent the top ranked correlations in the predefined MSigDB: H hallmark collections. The heatmap on the right in Fig. 5c–e shows the relative level of gene expression (red = high, blue = low) of the leading edge gene subset. NES scores, FDR-q values and up or downregulated genes as a consequence of NAP1L3 knockdown compared to control cells, are indicated in the diagrams (f). qPCR analysis of mRNA levels (normalised to UBC) of genes showing changes in expression in RNA-Seq of CD34+ HSPC UCBs cells transduced with shRNA against NAP1L3, relative to cells transduced with control vectors, 72 hours post transduction. The data is represented as the mean ± s.e.m., *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.001 (unpaired t-test), n = 3. (g–i) Flow cytometric quantification of mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of intracellular HOXA3 (g), HOXA5 (h) and HOXA9 (i), protein levels, of CD34+ HSPC UCBs cells transduced with shRNA against NAP1L3 or cells transduced with control vectors, 72 hours post transduction.